Weekend Study Flash Cards
There are a lot of good questions to reference here during the weekend, but go back into the rule books and look at these following rules. There is a lot more to look up and study but this is a good starting point if you don't have a ton of time. Every time you load these cards they will be randomly shuffled.
ABTH 100.4-100.16, 101.2-101.4, 102.1-102.3, 102.13-102.13.1, 103.3-103.5, 103.6.3, and 103.8.
GCOR 5.4, 5.8, 5.9, 6.4-6.6, 6.23, 6.27, 6.28, 6.32.2, 9.4-9.12, 9.17, 10.3, and 14.
Disclaimer, Monday through Thursday the weekend study button will disapear that way you don't get too fixated just on these questions. There is more to study during the week besides this cherry picked material.
Front #162
GCOR 6.4.1
When is permission required from the train dispatcher or control operator to make a reverse movement?
- When the reverse movement is within the same signaled block
- When a train or engine is advised that working limits have been established behind the train
- Permission is never required to make a reverse movement
- When the reverse movement will not remain in the same signaled block
Back #162
GCOR 6.4.1
Answer: When the reverse movement will not remain in the same signaled block
Feedback:Multiple trains can be traveling in the same authorized direction. Permission is needed to make a reverse outside the same signaled block to allow the dispatcher to stop an opposing train at a location to allow the reverse move to occur. Without this form of protection, the risk increases of a train making a reverse outside the same signaled block colliding with a following or opposing train.
Front #38
ABTH 103.8
To make an emergency brake application on a conventional train, move the automatic brake valve handle:
- Slowly to Emergency position and leave it there until the train stops. Lift the red cover of the Emergency Switch and activate the emergency valve on the HTD.
- Quickly to Emergency position and leave it there until the train stops. Lift the red cover of the Emergency Switch and activate the emergency valve on the ETD.
Back #38
ABTH 103.8
Answer: Quickly to Emergency position and leave it there until the train stops. Lift the red cover of the Emergency Switch and activate the emergency valve on the ETD.
Feedback:Quickly move the automatic brake valve to the Emergency position. While doing this, use the independent brake to develop desired brake cylinder pressure to help control slack. On conventional trains, activate the emergency valve on the ETD. By doing this, the emergency applications will start from both ends of the train, and move through the train faster, rather than waiting for it to travel from the head end all the way to the rear end.
Front #201
GCOR 6.32.2
The crew is notified that the automatic warning device has an activation failure, and a flagger is not at the crossing to provide warning. What is the train crew required to do?
- Stop and protect movement even if devices are seen to be working. After a crew member is on the ground at the crossing to warn traffic, proceed over the crossing at 15 mph.
- The train may proceed over the crossing, not exceeding 15 mph.
- Stop and protect movement even if devices are seen to be working. After a crew member is on the ground at the crossing to warn traffic, proceed over the crossing as directed by that crew member.
- The train must stop and protect the movement. If the device is seen to be working, train may proceed over the crossing, not exceeding 15 mph, until the head end of train completely occupies the crossing.
Back #201
GCOR 6.32.2
Answer: Stop and protect movement even if devices are seen to be working. After a crew member is on the ground at the crossing to warn traffic, proceed over the crossing as directed by that crew member.
Feedback:Because there is no flagger at the crossing to provide protection in one or both directions, the train must stop before fouling the crossing.
Front #84
ABTH 100.10B
When conducting a Class 1A air brake test, what percentage of the air brakes must be operative? Select the best answer.
- 97%
- 100%
- 90%
- 95%
Back #84
ABTH 100.10B
Answer: 100%
Feedback:At designated locations, trains may receive a Class 1A Air Brake Test. 100% of the brakes must be operative. Any cars that release prior to the signal being given can be retested once. To pass retest, brakes must remain applied for no less than 3 minutes.
Front #283
GCOR 14.3
A crew is operating in non-signaled territory with a track warrant stating "Work between MP 1 to MP 100 on the Main Track." The crew intends to release a portion of their authority. How must they release a portion of the track warrant?
- The release must begin at the inner limit of the authority.
- The release must begin at the outer limit of the authority.
- Track warrant cannot be released in increments.
- The crew may release any portion of their limits.
Back #283
GCOR 14.3
Answer: The release must begin at the outer limit of the authority.
Feedback:- You wouldn't want to release a portion of track in the middle of your limits because you could put yourself in a situation where you're occupying the main without authority. - For example: If this crew released from MP 50 to MP 70 and they were at MP 49, they would no longer have authority on the track to access MP 71 to MP 100.
Front #90
ABTH 100.14
A relief crew is on a train that had a crossing cut for more than 24 hours. What air brake test is required after the train is recoupled? Select the best answer.
- Class 1 air brake test on the entire train
- Class 3 air brake test
- An air brake test is not required
- Class 1 air brake test on the portion that was not coupled to the locomotive consist (off air)
Back #90
ABTH 100.14
Answer: Class 1 air brake test on the portion that was not coupled to the locomotive consist (off air)
Feedback:The portion of the train that was off air in excess of 24 hours will require a Class 1 air brake test.
Front #60
ABTH 100.9C
When using the Brake Pipe Leakage method, when must the train be inspected for leakage and retested?
- When leakage exceeds 4 psi
- When leakage exceeds 6 psi
- When leakage exceeds 5 psi
- When leakage exceeds 3 psi
Back #60
ABTH 100.9C
Answer: When leakage exceeds 5 psi
Feedback:While monitoring for one minute and the leakage exceeds 5 psi, the train must be inspected for leakage and re-tested. Gaskets, air hoses, and control valves can all contribute to excess leakage when they become faulty.
Front #311
GCOR 5.4.2A
Yellow flags warn trains to restrict movement due to:
- Public highway crossing at grade
- Railroad crossing at grade
- Men or equipment working on or near the tracks
- Track conditions or structures
Back #311
GCOR 5.4.2A
Answer: Track conditions or structures
Feedback:When used, yellow flags warn trains to restrict movement due to track conditions or structures. Temporary restrictions may be in effect for a variety of reasons. Examples of track conditions are wide gauge or a broken rail.
Front #315
GCOR 5.4.2B
One and a half miles after passing a yellow flag for a restriction not in effect, the crew passes a green flag. Does this green flag relieve the train of the yellow flag?
- No, the green flag must be at least four miles after the yellow flag.
- Yes, the green flag is at least one mile after the yellow flag.
- Yes, the green flag ends all speed restrictions.
- No, the green flag must be at least two miles after the yellow flag.
Back #315
GCOR 5.4.2B
Answer: No, the green flag must be at least two miles after the yellow flag.
Feedback:Yellow flags are to be displayed two miles before the restriction. The green flag would need to be at least that far from the yellow flag to apply in this scenario.
Front #314
GCOR 5.4.2B
What must the crew do when they are two miles beyond a yellow flag for a restriction that is not in writing?
- Stop.
- Proceed at restricted speed.
- Continue moving the train, not exceeding 10 mph.
- Stop, and then proceed at restricted speed.
Back #314
GCOR 5.4.2B
Answer: Continue moving the train, not exceeding 10 mph.
Feedback:When a yellow flag is displayed and the restriction is not specified in writing, once the train is two miles beyond the yellow flag, the train must continue moving not exceeding 10 mph. Yellow flags represent an upcoming restriction. Without specific information about the restriction, it's important to maintain a slower speed to avoid damage to the track or possible derailment.
Front #324
GCOR 5.4.5
If a series of locations require reduced speeds, the green flags could overlap yellow flags. Where will the green flag(s) be placed?
- At the end of the last speed restriction
- Green flags are not to be used for overlapping speed restrictions
- At the end of the first speed restriction
- At the end of each speed restriction
Back #324
GCOR 5.4.5
Answer: At the end of the last speed restriction
Feedback:- When a series of locations require reduced speeds, employees must place a yellow flag before each speed restriction and place a green flag at the end of the last speed restriction. - A final green flag after the last restriction can reduce confusion surrounding overlapping flags and reduce the possibility of speeding in a location with restrictions.
Front #250
GCOR 14.2B
Track warrant limits must be designated by specifying track, where required, and specific locations. Which of the following can be used as specific locations on a track warrant? (Select all that apply.)
- Switches
- Mileposts
- Railroad identifiable points
Back #250
GCOR 14.2B
Answer: - Switches - Mileposts - Railroad identifiable points
Feedback:When designating the limits on a track warrant, a switch (for example, ESS Reba), a milepost (MP 555), or a railroad identifiable point (Station Sign Hood) may be used to indicate the specific locations indicators.
Front #181
GCOR 6.5
A yard crew is about to make a shoving movement. The foreman has communicated with the engineer about how protection is being provided and instructs the engineer to back up 20 car lengths. The engineer acknowledges the instruction and begins the shoving movement. At what point must movement stop if the engineer receives no additional instructions?
- Movement must stop after exceeding five cars
- Movement must stop within the original specified distance
- Movement must stop within half the distance specified
- Once the movement has traveled 10 car lengths, the engineer must slow to 4 mph
Back #181
GCOR 6.5
Answer: Movement must stop within half the distance specified
Feedback:Stopping in half the distance specified can help prevent incidents and injuries if the person giving instructions becomes distracted or is unable to continue with instructions for any reason.
Front #336
GCOR 5.4.8
Flags must be displayed to the _____ of the track as viewed from an approaching train.
- left
- right
- bottom
- top
Back #336
GCOR 5.4.8
Answer: right
Feedback:- Flags must be displayed to the right of the track as viewed from an approaching train. - In multiple main track territory or where sidings are adjacent to main track(s), flags are placed on the field side of outside tracks. - Flags are placed in this manner unless otherwise specified by track bulletin, track warrant, special instructions, or general order. - Examples of track flagging are provided in Appendix A of the System Special Instructions
Front #325
GCOR 5.47
If instructions to proceed are received before the train stops, the train may pass the red flag without stopping.
- False
- True
Back #325
GCOR 5.47
Answer: True
Feedback:To avoid delays and congestion, a crew member must attempt to contact the employee in charge (EIC). The communication should include the milepost of the red flag and track being used. The EIC may offer instructions to proceed, only then may a train pass a red flag without stopping. There are often trains traveling in both directions and sometimes on multiple tracks through a Form B. It is important to confirm the instructions received are for the correct track and location.
Front #83
ABTH 100.11
A crew is preparing to depart the yard with cars to deliver to an industry 10 miles away. Which air brake test is required before departing?
- Class 1A Air Brake Test
- Transfer Train Air Brake Test
- Initial Terminal Air Brake Test
- Intermediate Air Brake Test
- Application and Release Air
Brake Test
Back #83
ABTH 100.11
Answer: Transfer Train Air Brake Test
Feedback:- A Transfer Train Air Brake Test is performed when a transfer train and yard movement does not exceed 20 miles in one direction. - To conduct the test, system must be charged to at least 60 psi as indicated by gauge or device at the rear of the train. - Make a 15 psi brake pipe reduction. - Verify brakes apply and remain applied on each car until a release signal is given.
Front #323
GCOR 5.4.5
What indicates the end of a temporary speed restriction?
- Yellow flag
- Red flag
- Yellow-red flag
- Green flag
Back #323
GCOR 5.4.5
Answer: Green flag
Feedback:Green flags indicate the end of temporary speed restrictions. Trains can resume track speed only after the rear wheels pass the green flag.
Front #304
GCOR 5.4.1
What do yellow flags indicate?
- Men or equipment working on the tracks
- Public highway crossing at grade
- Permanent speed restrictions
- Temporary speed restrictions
Back #304
GCOR 5.4.1
Answer: Temporary speed restrictions
Feedback:- Yellow flags are signals that warn of upcoming temporary speed restrictions. - Yellow flags are normally displayed two miles from a restriction. - However, they can be displayed less than two miles from a restriction in some cases.
Front #172
GCOR 6.4
This train has been given permission to make a reverse movement beyond the number plated signal. At what speed must the reverse movement be made?
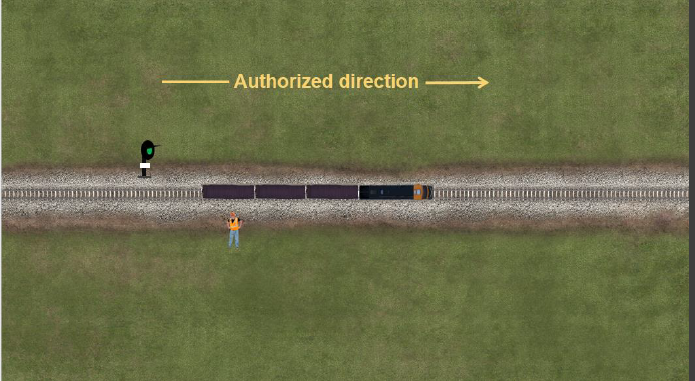
- 30 mph
- Restricted speed
- 20 mph
- Maximum authorized speed
Back #172
GCOR 6.4
Answer: Restricted speed
Feedback:All reverse movements must be made at restricted speed. The block signal indication in this scenario does not relieve the train crew from the requirements of moving at restricted speed. This signal does inform the crew that the block to the rear is clear of obstructions like a train, switch lined improperly, and broken rail to name a few.
Front #2
ABTH 103.4
An engineer notices the wheel slip light come on. The engineer reduces the throttle, but the light does not go out. What is required?
- Contact the train dispatcher to let him/her know that the outbound crew at the next terminal will need to inspect this
- Continue moving, but do not exceed throttle position 1
- Continue moving and come to a stop at the next available point where equipment can be set out
- Stop the train immediately and make sure the wheels are rotating freely
Back #2
ABTH 103.4
Answer: Stop the train immediately and make sure the wheels are rotating freely
Feedback:The train must not continue moving. Issues such as a locked wheel, slipped pinion gear, etc., may exist. Once stopped and someone is in position to observe the wheels, begin moving and determine if the wheels are moving freely.
Front #316
GCOR 5.4.3A
Two miles in advance of a track bulletin Form B, a yellow-red is used to warn a train to:
- Be prepared to call the employee in charge
- Slow down for track conditions and structures
- Slow down and watch out for men or equipment
- Be prepared to stop due to men and equipment
Back #316
GCOR 5.4.3A
Answer: Be prepared to stop due to men and equipment
Feedback:- Although crews should be attempting to contact the employee in charge (EIC) for permission through the limits, they must operate anticipating a stop. Depending on the train's speed and type, it could take almost two miles to stop. - That flag helps protect men and women working beyond it.
Front #269
GCOR 14.4
In signaled territory, which of the following conditions would allow the dispatcher to issue track warrants to multiple trains within the same limits?
- All trains are authorized to proceed in the same direction
- All the trains are high priority
- Track warrants can't be issued to multiple trains within the same limits
- All trains are authorized to leave switches in reverse position
Back #269
GCOR 14.4
Answer: All trains are authorized to proceed in the same direction
Feedback:The dispatcher would issue a Box 2 on the track warrant to designate the authorized limits. A Box 2 only allows for movement in one direction. The automatic block signals govern the movement and provide protection for the rear of each train.
Front #87
ABTH 100.13
Which scenario requires performing a running air brake test? Select the best answer.
- When the train leaves the yard
- When snow is up to or above the top of the rail
- When a train approaches 1,000 miles since the last Class 1 air brake test
- After departing from a signal requiring a stop
Back #87
ABTH 100.13
Answer: When snow is up to or above the top of the rail
Feedback:Performing a running air brake test during winter weather keeps the ice and snow from building up on the braking components. It is vital to ensure brakes are functioning properly and free of debris, particularly when icy rail conditions create additional challenges to braking safely.
Front #170
GCOR 6.4
Can a train moving on a yard track make a reverse movement?
- No
- Yes, with permission from the train dispatcher
- No, the train needs authority from the control operator
- A reverse movement cannot be made in non-signaled territory
Back #170
GCOR 6.4
Answer: No
Feedback:Reverse movements are not possible on a yard track because there is no authorized direction. No authority is required when moving in yard tracks (i.e., "other than main tracks"). GCOR 6.28, Movement on Other Than Main Tracks, governs how trains move while working within a yard. Reverse movements can be made on a main track, a controlled siding, or any track where a block system is in effect.
Front #7
ABTH 103.6.3
What is the preferred order when slowing or controlling speed?
- Dynamic braking
- Throttle manipulation; coast braking when conditions allow
- Dynamic braking supplementing with train air brakes
Back #7
ABTH 103.6.3
Answer: Throttle manipulation; coast braking when conditions allow, Dynamic braking, and Dynamic braking supplementing with train air brakes
Feedback:When possible, use the throttle only to achieve desired train speed. If throttle reduction alone is not sufficient, use dynamic braking and supplement with air brakes as necessary.
Front #8
ABTH 103.6.3A
Dynamic braking and air brakes are being used to slow for a permanent speed restriction. The slack is bunched on a level grade and the engineer has just released the air brakes. The engineer should maintain enough dynamic braking to keep the slack bunched until _____.
- Air brakes release on the first half of the train
- Air brakes release throughout the train
- Air brakes release on the head end locomotive consist
Back #8
ABTH 103.6.3A
Answer: Air brakes release throughout the train
Feedback:If the dynamic brakes are reduced before the air brakes release throughout the train, a run-out on the head end of the train is likely. The locomotives and head end of the train will start picking up speed, while cars near the rear end will not because the air brakes have not fully released.
Front #142
ABTH 103.3C
Before attempting a running release of the air brakes, the engineer must take into consideration which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
- Train make-up
- Temperature
- Physical characteristics of territory
- Train speed
Back #142
ABTH 103.3C
Answer: - Train speed - Train make-up - Temperature - Physical characteristics of territory
Feedback:If any of these operating conditions could lead to an unfavorable outcome with a running release, take the safe course and bring the train to a stop.
Front #351
GCOR 5.9.3
If the headlight and ditch lights both fail to operate at night, under what condition(s) can movement continue? (Select all that apply.)
- Use of another unit as lead unit
- None - all movement must stop
- Use of a white light on the lead unit
- The dispatcher provides approval
Back #351
GCOR 5.9.3
Answer: -Use of another unit as lead unit -Use of a white light on the lead unit
Feedback:At night, if headlight and ditch lights fail to operate and no other unit can be used as the lead unit, continue movement with a white light displayed on the lead unit.
Front #270
GCOR 14.4
In non-signaled territory, all trains authorized to proceed in the same direction must also move at what speed?
- Restricted speed
- Maximum authorized speed
- 20 MPH
- Reduced speed
Back #270
GCOR 14.4
Answer: Restricted speed
Feedback:In non-signaled territory, no devices are in place to help govern each train's movement, so regulating the speed of each train within the same limits is necessary to prevent collisions. Restricted speed ensures each train is moving at a speed that will allow them to stop within half the range of vision short of another train.
Front #39
ABTH 103.8
A train goes into emergency while moving. Which type of emergency brake applications must be reported to the train dispatcher?
- Only intentional emergency brake applications need to be reported.
- Both intentional and undesired emergency brake applications need to be reported.
- Only undesired emergency brake applications need to be reported.
- Emergency brake applications never need to be reported to the train dispatcher.
Back #39
ABTH 103.8
Answer: Both intentional and undesired emergency brake applications need to be reported.
Feedback:Whether intentional or undesired, emergency brake applications that occur while the train is moving must be reported to the train dispatcher. They are considered en route delays. Any undesired emergency brake applications that occur during normal service braking ("kickers," or "dynamiters") must be reported to the NOC Mechanical Help Desk as an air brake defect.
Front #326
GCOR 5.47
What does a red flag indicate?
- Trains must wait for permission from the dispatcher
- Where trains must stop
- Trains must move at restricted speed
- Trains can continue moving, not exceeding 10 mph
Back #326
GCOR 5.47
Answer: Where trains must stop
Feedback:A red flag is a form of protection for men and equipment working on the track. Permission from the employee in charge of the red flag is required before proceeding past it.
Front #347
GCOR 5.8.4
When can an employee sound the train horn? (Select all that apply)
- To warn pedestrians and animals of imminent injury or death
- To warn other train crews of an emergency situation
- To warn vehicle operators of potential property damage
- To warn others that an automatic warning device is out of service
Back #347
GCOR 5.8.4
Answer: -To warn other train crews of an emergency situation -To warn others that an automatic warning device is out of service -To warn pedestrians and animals of imminent injury or death -To warn vehicle operators of potential property damage
Feedback:After evaluating a situation, an employee may sound the train horn to provide warning to crews on other trains in an emergency situation. They may also use it to warn vehicle operators, pedestrians, trespassers, or animals in order to prevent imminent injury, death, or property damage.
Front #217
GCOR 9.6
The next signal is an absolute displaying an Approach Medium. Just before you pass the signal, it changes to red. How should you proceed?
- Continue prepared to pass next signal not exceeding 40 MPH
- Proceed prepared to stop at the next signal
- Stop immediately and contact the dispatcher
- Stop and then proceed at 20 MPH
Back #217
GCOR 9.6
Answer: Stop immediately and contact the dispatcher
Feedback:When operating on any proceed indication that downgrades to a stop, the potential exists that another train or piece of equipment is now occupying that block. The signal could also drop as a result of broken rail ahead. Stopping is required to avoid an incident and ensure the safety of anyone working in those blocks. Contact the dispatcher so they can help determine the cause and provide instructions on how to proceed.
Front #31
ABTH 100.9A
Which of the following scenarios require a Brake Pipe Leakage Test to be performed?
- After changing operating ends of a locomotive consist
- During a Transfer Train Air Brake Test
- After removing the rear locomotive of a locomotive consist
- During an Initial Terminal and Road Air Brake Test
Back #31
ABTH 100.9A
Answer: During an Initial Terminal and Road Air Brake Test
Feedback:Remember, there are three air brake tests that require a leakage test: - Class 1 Air Brake Test - Class 1 Air Brake Test from Yard Test Plant - Class 1A Air Brake Test A Leakage Test is also required when adding cars not pretested to a train. The preferred method for testing brake pipe leakage is the Air Flow Method (AFM).
Front #130
ABTH 102.13
Which of the following fulfills the requirement for emergency application capability from the rear of the train? Select all that apply.
- Distributed power placed at the front of the train
- An armed and tested operative two-way endof- train telemetry system (HTD/ETD)
- Distributed power placed on the rear of the train
- Trains manned by an employee providing visual signals
Back #130
ABTH 102.13
Answer: - An armed and tested operative two-way endof- train telemetry system (HTD/ETD) - Distributed power placed on the rear of the train
Feedback:Trains with a manned helper, caboose, or passenger equipment at the rear of the train that is equipped with an emergency brake valve and manned by an employee equipped with two-way voice radio communication with the engineer at the head of the train also fulfill this requirement.
Front #93
ABTH 101.2A
Whose responsibility is it to ensure each locomotive in their charge is inspected each day the locomotive is in service?
- NOC mechanical
- Locomotive engineer
- Engineer and conductor
- Mechanical foreman
Back #93
ABTH 101.2A
Answer: Locomotive engineer
Feedback:Engineers have the responsibility to ensure each locomotive in their charge is inspected each day the locomotive is in service. This includes locomotives picked up en route.
Front #30
ABTH 100.9A
A conventional train is performing the brake pipe leakage test using the AFM method. The ETD is indicating there is 85 psi on the rear of the train. Once the air flow does not exceed____ CFM, the test is complete.
- 75
- 90
- 60
- 15
Back #30
ABTH 100.9A
Answer: 60
Feedback:If the flow exceeds 60 CFM, the train needs to be inspected for leakage. Leakage is often the result of a bad gasket or air hose. For DP trains: When combined air flow readings of DP lead and DP remotes do not exceed 90 CFM, the test is complete.
Front #261
GCOR 14.10
A track warrant is in effect until a crew member reports the train has cleared the limits or __________________.
- The track warrant is made void
- The track warrant has an OK time
- The engineer and conductor have a briefing about the location of their train
- The engineer and conductor have a briefing about the limits being released
Back #261
GCOR 14.10
Answer: The track warrant is made void
Feedback:A track warrant is in effect until a crew member reports the train has cleared the limits or the track warrant is made void.
Front #71
ABTH 100.10A
Who is permitted to perform a Class 1 air brake test/inspection on freight trains?
- Only a qualified mechanical inspector
- Only a qualified employee
- Both roles
Back #71
ABTH 100.10A
Answer: Both roles
Feedback:Both qualified employees and qualified mechanical inspectors may perform Class 1 air brake test/inspection on freight trains. Conductors are considered qualified employees. Carmen are qualified mechanical inspectors who receive more extensive training.
Front #24
ABTH 103.6.3F
When is stretch braking permitted?
- Only when operating on territory that does not have any heavy and/or mountain grades.
- Only when more fuel-efficient methods will not provide the necessary control of train speed.
- Only on trains that have a TOB greater than 100.
- Stretch braking is always permitted.
Back #24
ABTH 103.6.3F
Answer: Only when more fuel-efficient methods will not provide the necessary control of train speed.
Feedback:More fuel-efficient methods include throttle manipulation, dynamic braking, and dynamic braking supplemented with air brakes. If none of these will provide necessary control of train speed, then stretch braking is permitted.
Front #317
GCOR 5.4.3A
How long before and after a track bulletin Form B may yellow-red flags be displayed?
- Four hours
- Two hours
- Three hours
- One hour
Back #317
GCOR 5.4.3A
Answer: One hour
Feedback:This only allows the employee in charge to put up their flags before the Form B takes effect, which gives them the full time of the Form B to work.
Front #305
GCOR 5.4.1
What does a yellow-red flag indicate?
- Where a train may be required to go slow
- When a train may be required to stop
- When a train is required to stop
Back #305
GCOR 5.4.1
Answer: When a train may be required to stop
Feedback:- Yellow-red flags indicate when a train may be required to stop. - This flag also indicates that you should be on the radio reaching out to the employee in charge for permission through their Form B limits.
Front #89
ABTH 100.14
A train is stopped in a siding and has cut a road crossing to avoid blocking traffic. Three hours later, the crew recouples the train and is ready to depart. Which air brake test is required before departing? Select the best answer.
- Running air brake test
- Application and release air brake test
- Intermediate air brake test
- Air brake test when cutting off and recoupling
Back #89
ABTH 100.14
Answer: Air brake test when cutting off and recoupling
Feedback:This test is only applicable if the time has not exceeded 24 hours. The brake pipe has not been compromised by cutting the road crossing. The train is being put back together the same way it was before being uncoupled.
Front #10
ABTH 103.6.3E
List, in order, the steps to slow or control train speed by using throttle modulation in a sag or undulating grade.
- As you approach the sag, reduce throttle as necessary to control train speed.
- Just before the head end of the train reaches the ascending grade, increase the throttle.
- Reduce the throttle as the rear of
the train approaches the
ascending grade.
- Reduce the throttle further as the head end of the train begins descending.
- Continue to increase the throttle as the train ascends the grade.
Back #10
ABTH 103.6.3E
Answer: 1. As you approach the sag, reduce throttle as necessary to control train speed. 2. Reduce the throttle further as the head end of the train begins descending. 3. Just before the head end of the train reaches the ascending grade, increase the throttle. 4. Continue to increase the throttle as the train ascends the grade. 5. Reduce the throttle as the rear of the train approaches the ascending grade.
Feedback:Knowing where the entire train is (rear end) in relation to the sag or undulating grade is important here. As the head end of the train approaches the ascending grade, increase throttle before it reaches the grade in order to build some momentum.
Front #4
ABTH 100.4
What is the minimum percentage of the air brakes that must be operative when enroute?
- 95%
- 98%
- 90%
- 100%
Back #4
ABTH 100.4
Answer: 95%
Feedback:While there is allowance for some mechanical failures, we must keep it to a minimum for safety. Inoperative brakes can impact how a train handles and increase the distance it could take to stop
Front #230
GCOR 9.11
You are stopped where CTC ends and non-signaled TWC begins. You have been verbally authorized beyond the signal and have a track warrant to continue. How must you proceed?
- Not exceeding 20 mph for 2 miles or until the leading wheels pass the opposing distant signal
- Restricted speed until the leading wheels have passed the next governing signal
- Restricted speed for 2 miles or until the leading wheels pass the opposing distant signal
- Restricted speed until the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
Back #230
GCOR 9.11
Answer: Restricted speed for 2 miles or until the leading wheels pass the opposing distant signal
Feedback:The previous signal required restricted speed, but you are leaving block system limits beyond that signal. GCOR 9.11 requires the train move at restricted speed for 2 miles or until the leading wheels pass the opposing distant signal.
Front #349
GCOR 5.9.1
The headlight must be set to bright at the front of every train. When must they be dimmed? (Select all that apply.)
- Left unattended on a main track in non-signaled territory
- Approaching and passing the head end of a train at night
- Stopped on the main track waiting for an approaching train
- Stopped close behind a train
Back #349
GCOR 5.9.1
Answer: - Stopped close behind a train - Left unattended on a main track in non-signaled territory - Stopped on the main track waiting for an approaching train - Approaching and passing the head end of a train at night
Feedback:- All of these are correct - There are six times when we dim the headlight. The other two times are: - At stations and yards where switching is being done - To permit passing of hand signals or when the safety of employees requires
Front #169
GCOR 6.4
On which tracks can reverse movements be made? (Select all that apply.)
- Controlled siding
- A siding in track warrant control (TWC) territory
- Main track
- Any track where block system is in effect
Back #169
GCOR 6.4
Answer: - Main track - Controlled siding - Any track where block system is in effect
Feedback:Reverse movements can only be made where main track rules are applicable. There is always an authorized direction on main tracks and controlled sidings unless the train crew has been given bidirectional authority. A reverse move cannot be made if bidirectional authority has been granted.
Front #29
ABTH 100.9A
There are two methods used to conduct a Brake Pipe Leakage Test. In both methods, you need to charge the brake system to within ____ of the regulating valve as indicated by a gauge or device at the rear of the train.
- 20 psi
- 90 psi
- 15 psi
- 10 psi
Back #29
ABTH 100.9A
Answer: 15 psi
Feedback:Regulating valve settings: - Freight service = 90 psi - Passenger service = 105 psi - The pressure at rear of train must be within 15 psi of the pressures listed above. - The pressure at rear of the train must be determined by one of the following: A gauge verified to be accurate, an ETD, or a DP locomotive consist.
Front #262
GCOR 14.10
A track warrant instructs the crew to clear the main track by 1000. The switch that will be used to clear the main track is defective, and the crew is unable to contact the dispatcher on radio. Which statement below is true?
- If an employee cannot contact the train dispatcher and the time limit expires, authority is extended and there is no need to contact the train dispatcher
- If an employee cannot contact the train dispatcher and the time limit expires, authority is extended for another hour until the train dispatcher is contacted
- If an employee cannot contact the train dispatcher and the time limit expires, authority is extended until the train dispatcher is contacted
- If an employee cannot contact the train dispatcher and the time limit expires, your authority expires, and you will need to report to the train dispatcher.
Back #262
GCOR 14.10
Answer: If an employee cannot contact the train dispatcher and the time limit expires, authority is extended until the train dispatcher is contacted
Feedback:Time limits are often given to trains needing to perform work online such as switching or servicing industries. An expedited freight train en route that can't be delay may cause the dispatcher to request you to be clear by a specific time to allow the freight train to pass.
Front #3
ABTH 103.4
A crew on a conventional train is traveling at 30 mph in throttle position 4 and is approaching a railroad crossing at grade (diamond). When may the engineer advance the throttle to a position higher than notch 4?
- Once the lead locomotive passes over the railroad crossing at grade (diamond)
- Once the entire train passes over the railroad crossing at grade (diamond)
- Once the leading wheels pass over the railroad crossing at grade (diamond)
- Once the entire locomotive consist passes over the railroad crossing at grade (diamond)
Back #3
ABTH 103.4
Answer: Once the entire locomotive consist passes over the railroad crossing at grade (diamond)
Feedback:Most railroad crossings at grade are not smooth. Waiting to advance the throttle after the locomotive consist passes over will help to prevent any sort of surge and make for better train handling.
Front #174
GCOR 6.6
Before requesting or making a back-up movement, who must perform a job safety briefing?
- Only the engineer and conductor
- All crew members
- A crew member and the control operator/dispatcher
- Engineer and the foreman in charge
Back #174
GCOR 6.6
Answer: All crew members
Feedback:Notice this briefing has to occur before asking the dispatcher for permission. The train crew must be on the same page on all aspects of this move. Once the crew completes their JSB, they can clearly communicate to the dispatcher about the move and that all safeguards have been discussed and put in place.
Front #202
GCOR 6.32.2
Under which conditions must movement not foul a crossing equipped with an automatic crossing warning device until the device has been operating long enough to provide warning, and the crossing gates, if equipped, are fully lowered? (Select all that apply.)
- Movement is on the main track
- Movement is on other than main track or siding
- Movement is closely following another movement
- Movement has stopped within 3,000 feet of the crossing
Back #202
GCOR 6.32.2
Answer: - Movement has stopped within 3,000 feet of the crossing - Movement is closely following another movement - Movement is on other than main track or siding
Feedback:The purpose of this rule is to ensure the warning device at a crossing does not deactivate prior to the train occupying the crossing. For situations applying to any of the three correct answers, the automatic warning device would have ample time to deactivate before the train reached the crossing
Front #228
GCOR 9.9B
You entered a block on a clear signal at 10 mph while traversing a Form A. In doing so, your speed dropped to as low as 7 mph. How are you required to proceed to the next signal?
- Proceed at restricted speed until the leading wheels pass the next signal, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
- Proceed at reduced speed until the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
- Proceed prepared to stop at the next signal until the next signal is visible and that signal displays a Proceed indication
- Proceed at restricted speed until the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
Back #228
GCOR 9.9B
Answer: Proceed prepared to stop at the next signal until the next signal is visible and that signal displays a Proceed indication
Feedback:- Delayed in a block means that you have either stopped, or your speed is reduced to below 10 mph. - Delayed in a block only applies if the block has been entered on a signal that does not require restricted speed. - If the previous signal required restricted speed, then GCOR 9.11 is applicable.
Front #173
GCOR 6.6
A crew calls the dispatcher for permission to make a back-up movement. Which of the following does the dispatcher need to verify within same or overlapping limits? (Select all that apply.)
- A main track is not removed from service by a track bulletin
- Another authority is not in effect unless conflicting movements are protected
- Permission to leave a switch in the reverse position has not been granted
- A track bulletin Form B is not in effect
Back #173
GCOR 6.6
Answer: - Another authority is not in effect unless conflicting movements are protected - A track bulletin Form B is not in effect - A main track is not removed from service by a track bulletin - Permission to leave a switch in the reverse position has not been granted
Feedback:The dispatcher is verifying that there are no trains, maintenance of way employees, or any piece of railroad equipment (switch, track) that will impede the safety of the train making the back-up move. A back-up movement does not require visual protection from the train crew.
Front #346
GCOR 5.8.4
When can whistle signal (#7) be designated within whistle quiet zones approaching public crossings?
- Automatic warning devices are malfunctioning or out of service
- A train is approaching roadway workers
- During an emergency
Back #346
GCOR 5.8.4
Answer: -Automatic warning devices are malfunctioning or out of service -During an emergency
Feedback:Whistle signal (7) can be designated within whistle quiet zones approaching public crossings only when it is necessary to provide warning during an emergency, when automatic warning devices are malfunctioning or out of service, or when the whistle quiet zone is not in effect.
Front #5
ABTH 100.8
Which of the following may be used to verify air brake pressure at the rear of a train? (Select all that apply.)
- A DP locomotive
- A gauge verified to be accurate
- Application and Release Test
- An ETD (end-of-train device)
Back #5
ABTH 100.8
Answer: A DP locomotive, a gauge verified to be accurate, and an ETD (end-of-train device)
Feedback:When performing air brake tests and verifying the train is complete, the crew must ensure the brake pipe has continuity all the way through the train. A DP locomotive, ETD, or handheld gauge can all be used to determine the air pressure on the rear. If using a handheld gauge, it must be verified accurate within the last 92 days.
Front #312
GCOR 5.4.2A
When yellow flags are used and they are displayed less than two miles from the restricted area, how is this communicated to the crew?
- This information is included in the track bulletin.
- This information is included in the track warrant.
- This information is included in a general order.
- This information is included in a general notice.
Back #312
GCOR 5.4.2A
Answer: This information is included in the track bulletin.
Feedback:- When the restricted area is close to a terminal, junction, or another area, or if restriction is on a siding, employees will display the yellow flag less than two miles before the restricted area. - This information is also included in the track bulletin, track warrant, or general order. - BNSF uses a General Track Bulletin to deliver track bulletins.
Front #266
GCOR 14.1
How would you determine which authorities are in effect on any subdivision?
- GCOR Chapter 14 (TWC Rules)
- System General Notice
- System Special Instructions
- Timetable
Back #266
GCOR 14.1
Answer: Timetable
Feedback:You can locate the authorities in effect on the subdivision by looking one of the following: - Type of Operation column on the timetable schedule page - Item 3 in timetable special instructions
Front #37
ABTH 103.8
When conditions warrant, use an emergency brake application in conditions where there is doubt that service applications can control train speed, and maximum authorized speed is exceeded by _________ or more.
- 10 mph
- 1 mph
- 5 mph
- 3 mph
Back #37
ABTH 103.8
Answer: 5 mph
Feedback:If maximum authorized speed is exceeded by five mph or more and you are not sure a service brake application can control train speed, don't hesitate to place the train into emergency.
Front #143
ABTH 103.3C
When performing a running release of the air brakes, which of the following is true?
- Increase brake pipe reduction to 15 psi and allow the exhaust at the automatic brake valve to stop before releasing the brakes.
- Increase the brake pipe reduction to 10 psi, and after the exhaust at the automatic brake valve stops, wait an additional 30 seconds before releasing the brakes.
- Increase brake pipe reduction to 10 psi and allow the exhaust at the automatic brake valve to stop before releasing the brakes.
- Increase the brake pipe reduction to 15 psi, and after the exhaust at the automatic brake valve stops, wait an additional 30 seconds before releasing the brakes.
Back #143
ABTH 103.3C
Answer: Increase brake pipe reduction to 10 psi and allow the exhaust at the automatic brake valve to stop before releasing the brakes.
Feedback:A10 psi brake pipe reduction will allow for an accelerated service release of the brakes when the automatic brake valve is moved to the Release position. Accelerated service release cuts release times in half and greatly reduces in-train forces. Wait for the exhaust to stop before moving the automatic brake to release to allow for the air to travel through the entire brake pipe.
Front #227
GCOR 9.9A
A train operating in ABS on a clear signal stops to make a set out. Once the set out is complete, how should the train proceed to next signal?
- At reduced speed until the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
- At restricted speed until the leading wheels pass the next signal, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
- At restricted speed until the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
- At maximum authorized speed prepared to stop at the next governing signal
Back #227
GCOR 9.9A
Answer: At restricted speed until the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
Feedback:Multiple trains can be authorized in the same limits in ABS provided they are all moving in the same direction. GCOR 9.17 allows a train authorized on the main track to open a switch, wait 5 minutes, and then proceed on to the main track if they do not hear or see movement approaching. A train that has been delayed could potentially encounter another train that has complied with 9.17.
Front #282
GCOR 14.3
A train operating in non-signaled territory receives a track warrant with a box 4 "Work between MP 1 to MP 100 on the Main Track." In which direction is the train authorized?
- Southward only
- Both directions
- Westward only
- Northward only
- Eastward only
Back #282
GCOR 14.3
Answer: Both directions
Feedback:- Box 2 track warrants instruct to proceed from one point to the other, indicating the authority is in one direction only. - Box 4 track warrants indicate no direction in the address line. They are instructed to work between two specific points, indicating the authority is bidirectional.
Front #271
GCOR 14.4
When operating under a track warrant, what instructions must you follow if Yard Limits are in effect?
- Track Warrants are not issued in Yard Limits
- Track and Time instructions
- Yardmaster instructions
- Track Warrant instructions
Back #271
GCOR 14.4
Answer: Track Warrant instructions
Feedback:If you are issued a track warrant while operating in Yard Limits or Restricted Limits, you will still comply with the terms of those authorities, but the instructions on the track warrant must be followed.
Front #129
ABTH 102.13
Which of the following trains are exempt from the rule requiring the capability to initiate an emergency brake application from the rear of the train? Select all that apply.
- Engines without cars
- A road switcher that is designated as a key train
- A work train that weighs 4,500 tons and is operating on a 2% or steeper grade as listed in BNSF SSI, Item 2(A)
- A local train that weighs 3,000 tons operating on .5% grade and is traveling a distance that can be operated by a single crew in a single tour of duty
Back #129
ABTH 102.13
Answer: - Engines without cars - A local train that weighs 3,000 tons operating on .5% grade and is traveling a distance that can be operated by a single crew in a single tour of duty
Feedback:Trains designated as key trains must have the capability to initiate an emergency brake application from the rear of train. Key train status can change over the course of a trip due to setouts and pickups made en route. It is the responsibility of the train crew to know the key train status.
Front #144
ABTH 103.3B
A crew pulling into a siding stops to meet another train. When operating conditions allow, increase brake pipe reduction to at least ___ psi.
- 26
- 15
- 20
- No brake pipe reduction is needed if the independent brakes can hold the train stationary.
Back #144
ABTH 103.3B
Answer: 15
Feedback:Making a 15 psi reduction will ensure an accelerated service release when air brakes are released. The reduction also allows the engineer to verify pressure rises at the rear when releasing brakes, validating that air is flowing through the train.
Front #12
ABTH 103.6.3C
When using throttle reduction to slow/control speed on an ascending grade, gradually reduce the throttle _______.
- One notch at a time
- As quickly as needed
- Waiting a minimum of 10 seconds between each throttle notch reduction
Back #12
ABTH 103.6.3C
Answer: One notch at a time
Feedback:Plan ahead and allow the grade to work in your favor when slowing uphill. It's important to avoid methods that might prevent the train from maintaining a stretched condition, such as dynamic braking.
Front #339
GCOR 5.8.1
Which of the following are instances of when you should ring your engine bell? (Select all that apply.)
- When approaching railroad crossings at grade
- When approaching men or equipment on or near the track
- When whistle signal (7) is required
- When operating in Track and Time
Back #339
GCOR 5.8.1
Answer: - When approaching men or equipment on or near the track - When whistle signal (7) is required
Feedback:- If you are required to whistle for a road crossing, you are also required to have your bell on. - For this reason, the bells on newer locomotives are automatically turned on.
Front #350
GCOR 5.9.3
Headlight failures must be reported to the:
- Supervisor
- Dispatcher
- Conductor
- Nearest police department
Back #350
GCOR 5.9.3
Answer: Dispatcher
Feedback:Headlight failure must be reported to the dispatcher so they can make arrangements for repairs. This also allows them to plan for any delays that might occur as a result of the headlight failure. If the train is equipped with ditch lights, they must also be on if the headlight fails in order to provide some visibility for the crew and others.
Front #28
ABTH 100.9A
What are the two methods used to perform a Brake Pipe Leakage Test?
- Class 3 Air Brake Test, 20 lb. brake pipe reduction
- Class 3 Air Brake Test, Air Flow Method (AFM)
- Air Flow Method (AFM), Brake Pipe Leakage Method
- Class 1 Air Brake Test, 20 lb. brake pipe reduction
Back #28
ABTH 100.9A
Answer: Air Flow Method (AFM), Brake Pipe Leakage Method
Feedback:The Air Flow Method (AFM) is the preferred method for performing a Brake Pipe Leakage Test when the locomotive has an air flow meter. The Brake Pipe Leakage Method - which has 9 steps to determine the amount of leakage in your brake pipe system - is to be used when the AFM gauge is not on the locomotive.
Front #182
GCOR 6.5
A train working in joint Track and Time will make a one-mile shoving movement. Maximum timetable speed is 45 mph. What is the maximum speed at which the cars can be shoved?
- Restricted speed
- 40 mph
- 20 mph
- 45 mph
Back #182
GCOR 6.5
Answer: Restricted speed
Feedback:The maximum speed when shoving in the direction authorized is 20 mph for freight trains. This train has Track and Time and therefore authority to move in both directions. When shoving, it is in the direction authorized. However, the Track and Time is joint. Movements within joint authority must be made at restricted speed regardless of the direction authorized.
Front #163
GCOR 6.4.1
If this train was in non-signaled territory, would it need permission to make a reverse movement?

- A reverse movement cannot be made in non-signaled territory
- No, as long as the train is within the same signaled block
- Yes
Back #163
GCOR 6.4.1
Answer: Yes
Feedback:Permission must always be obtained in non-signaled territory because there are no block signals to protect the train in either direction.
Front #280
GCOR 14.3
An eastbound train has a track warrant with a box 2: "Proceed from Manteca to ESS Axilla on the Main Track." Is the crew allowed to foul the ESS Axilla?
- Yes, but only if another train isn't in the immediate area
- No, the crew must stop prior to fouling the ESS Axilla
- Yes, ESS Axilla is listed as the last named point, so the crew can foul and operate the train over the switch
Back #280
GCOR 14.3
Answer: No, the crew must stop prior to fouling the ESS Axilla
Feedback:- In this example, the eastbound train must stop prior to fouling the ESS Axilla - A train that is traveling westbound would be able to use the ESS Axilla to clear the main track - GCOR 14.3 states, "A train or engine must not foul a switch at either end of the limits where an opposing train may use the same switch to clear the main track"
Front #313
GCOR 5.4.2A
The speed specified by a track bulletin Form A restriction must not be exceeded until:
- The head end of the train clears the yellow flag
- The head end of the train clears the restricted area
- The rear of the train clears the yellow flag
- The rear of the train clears the restricted area
Back #313
GCOR 5.4.2A
Answer: The rear of the train clears the restricted area
Feedback:The entire train must clear the restricted area before the train can increase speed. It isn't safe to increase speed while any portion of the train remains in the restricted area.
Front #13
ABTH 103.6.3D
When using throttle reduction to slow/control train speed while cresting grade, continue to reduce throttle to keep the speed from increasing until _______.
- The lead locomotive consist has crested the grade
- The leading wheels have crested the grade
- At least half the train has crested the grade
- The rear wheels have crested the grade
Back #13
ABTH 103.6.3D
Answer: At least half the train has crested the grade
Feedback:A distance counter is useful in this scenario in the event a visual is not on the screen. If increasing speed when going over a steep hill, the chances of breaking the train in two greatly increases. A good resource for determining when half the train is over the peak of the grade is using the distance counter.
Front #196
GCOR 6.27
Which of the following locations could restricted speed be applicable? (Select all that apply.)
- Yard track
- Siding in TWC territory
- Main track
- Controlled siding
Back #196
GCOR 6.27
Answer: - Main track - Controlled siding
Feedback:- Restricted speed only applies where main track rules are applicable. - A siding in CTC territory is controlled by a control operator; main track rules apply there. - A siding in TWC territory is considered a non-controlled siding, and therefore, other than main track. Restricted speed does not apply there.
Front #322
GCOR 5.4.3B
With no red flag displayed two miles beyond a yellow-red flag for a track bulletin Form B that is not in effect, the train moves at restricted speed. When may the train increase speed? (Select all that apply.)
- When the leading wheels of movement pass a green flag.
- When the leading wheels of movement are four miles beyond the yellow-red flag, and the train dispatcher verifies that no track bulletin or track warrant protecting men or equipment is in effect at that location.
- After a crew member receives instructions from the employee in charge.
- After the rear of the train passes a green flag.
Back #322
GCOR 5.4.3B
Answer: - After a crew member receives instructions from the employee in charge. - When the leading wheels of movement are four miles beyond the yellow-red flag, and the train dispatcher verifies that no track bulletin or track warrant protecting men or equipment is in effect at that location.
Feedback:- If no red flag is displayed and no instructions have been provided by the employee in charge of the yellow-red flag, move at restricted speed. - Increase speed only after a crew member receives instructions from the employee in charge, or the leading wheels of movement are four miles beyond the yellow-red flag, and the train dispatcher verifies that no track bulletin or track warrant protecting men or equipment is in effect at that location. - Some Form Bs can be several miles long. Always err on the side of safety.
Front #216
GCOR 9.4
If a light is absent, a white light is displayed where a colored or lunar light should be, or additional colored or lunar lights are displayed, how must you regard the signal?
- Proceed at maximum authorized speed and report the issue to the dispatcher
- Stop, and then proceed at restricted speed and report the issue to the dispatcher
- Regard that signal as displaying the most restrictive indication it can give
- Proceed at reduced speed until you pass the next governing signal
Back #216
GCOR 9.4
Answer: Regard that signal as displaying the most restrictive indication it can give
Feedback:If a light is dark or just a lightbulb without a lens is seen, regard that block or interlocking signal as displaying the most restrictive indication it can give. In most cases, this indicates either stop or restricted speed.
Front #82
ABTH 100.10.1
To be qualified as an extended haul train, what is the maximum number of pickups and setouts allowed between Class 1 and Class 1A inspection points?
- One pickup, one setout
- Two pickups, two setouts
- One pickup, two setouts
- Two pickups, one setout
Back #82
ABTH 100.10.1
Answer: One pickup, one setout
Feedback:- Combining/splitting of two extended haul trains does not count as a pickup or set out. - Setting out defective equipment discovered en route does not count as a set out. - Cars or solid block of cars added en route must be pretested by a Qualified Mechanical Inspector (QMI). - Train must not move any cars with defective equipment unless cleared by the NOC Mechanical Help Desk.
Front #268
GCOR 14.7
When reporting past a specific location in TWC, what communication must occur?
- Engineer and conductor job brief and agree on train's location. Engineer and conductor will communicate with dispatcher.
- Conductor and dispatcher job brief and agree on train's location. The engineer then reports clear.
- Engineer and dispatcher job brief and agree on train's location. The conductor then reports clear.
- Conductor reports location head end has passed to dispatcher.
Back #268
GCOR 14.7
Answer: Engineer and conductor job brief and agree on train's location. Engineer and conductor will communicate with dispatcher.
Feedback:The engineer and conductor are jointly responsible. This communication helps reduce the possibility of releasing the wrong location and giving up track the train is still occupying.
Front #166
GCOR 6.4.2A
The trailing end of this train is stopped between the outer opposing absolute signals of the control point. Can it change direction without permission?

- Yes, permission from control operator is only required when the leading end stops between the outer opposing signals of the control point
- Yes, as long as the train is within the same signaled block
- No, permission from the control operator is required
Back #166
GCOR 6.4.2A
Answer: No, permission from the control operator is required
Feedback:- The key point is that this is the trailing end of the movement. - The trailing end could be the locomotive depending on which way the train is moving. - Signals cannot change aspects while within the control points, however, the switch can be lined for a different route. - The switch is on a different circuit than the signals, so the control operator can still line the switch while the train is within the control points.
Front #229
GCOR 9.9.1
You are proceeding at 20 mph and have passed the approach signal to an automatic interlocking which indicates Proceed. How is your train required to move?
- Proceed prepared to stop at the automatic interlocking
- Proceed at restricted speed until leading wheels pass the automatic interlocking
- Proceed prepared to pass next signal at 40 mph
- Proceed at maximum authorized speed
Back #229
GCOR 9.9.1
Answer: Proceed prepared to stop at the automatic interlocking
Feedback:When passing a signal that governs the approach to an automatic interlocking below 25 mph, or if after passing that same signal your speed falls below 25 mph, you must be prepared to stop at the automatic interlocking until the train is within a 1,000 feet of the interlocking. A conflicting movement may arrive at the interlocking before you get the Proceed indication first.
Front #108
ABTH 102.1
Which factors determine the number of hand brakes or cars that need to be secured? Select all that apply.
- Number of loaded and empty cars
- Grade and adhesion
- Weather conditions
- Time of day
Back #108
ABTH 102.1
Answer: - Grade and adhesion - Number of loaded and empty cars - Weather conditions
Feedback:Refer to the train list/work order to determine the number of loaded and empty cars in the train. Refer to the timetable for the grade of the track.
Front #198
GCOR 6.27
When required to move at restricted speed, how long must a train remain at that speed?
- Until the trailing end of the train passes the next governing signal
- Until the rear wheels reach a point where restricted speed is no longer required.
- Until the next signal is visible, and it displays a Proceed indication
- Until the leading wheels reach a point where restricted speed is no longer required
Back #198
GCOR 6.27
Answer: Until the leading wheels reach a point where restricted speed is no longer required
Feedback:Restricted speed is always a head end restriction. It requires looking for and being prepared to stop short of certain things within a specific area. Once the leading wheels pass the point where it is no longer required, trains can resume speed.
Front #165
GCOR 6.4.2
When can a movement change direction without permission from the train dispatcher or control operator?
- When movement stops with the trailing end between the outer opposing absolute signals of a control point.
- When movement continuously occupies at least one car length of the limits at an automatic interlocking.
- When movement stops with the trailing end between the outer opposing absolute signals of a manual interlocking.
Back #165
GCOR 6.4.2
Answer: When movement continuously occupies at least one car length of the limits at an automatic interlocking.
Feedback:A movement may change direction within the limits of an automatic interlocking if it continuously occupies at least one car length of the limits. If movement stops while the trailing end is between the outer opposing absolute signals of a control point or manual interlocking, the movement must not change direction without permission from the control operator.
Front #352
GCOR 5.9.3
To protect the public at crossings during a nighttime headlight failure, a crew member on the ground must provide warning until the crossing is occupied unless: (Select all that apply.)
- No traffic is stopped at the crossing
- Crossing lights are flashing
- Crossing gates are fully lowered
- No traffic is approaching the crossing
Back #352
GCOR 5.9.3
Answer: -Crossing gates are fully lowered -No traffic is stopped at the crossing -No traffic is approaching the crossing
Feedback:Stopping the train at public crossings and providing warning via crew member when it is dark can prevent the public from failing to see an oncoming locomotive. The crew member on the ground must provide warning until the crossing is occupied unless: - Crossing gates are in the fully lowered position. or - No traffic is approaching or stopped at the crossing.
Front #95
ABTH 101.2C
Once a locomotive daily inspection is conducted, complete the 229.21 locomotive cab card. What else is required to complete before ending your tour of duty?
- An Electronic Class 1 Air Brake Test Report
- An Electronic ETD Armed Report
- An Electronic Device Inspection Report
- An Electronic Locomotive Inspection Report
Back #95
ABTH 101.2C
Answer: An Electronic Locomotive Inspection Report
Feedback:When conducting a locomotive daily inspection and completing the locomotive cab cards, be sure to also complete the electronic locomotive inspection report on the tie-up screen.
Front #92
ABTH 100.16
When at terminals where facilities are available for immediate air brake inspections and repairs, an inbound train inspection may be required. Which is the required automatic brake handle position to reduce the brake pipe pressure to near 0 psi for the inbound train inspection?
- Suppression
- Release
- Handle off/Continuous service
- Emergency
Back #92
ABTH 100.16
Answer: Handle off/Continuous service
Feedback:A valid inbound inspection requires the pressure be reduced at a service rate. Handle off/Continuous service reduces at that rate. The Emergency position will also draw the brake pipe pressure down to 0 psi, but at the much faster emergency rate.
Front #61
ABTH 100.9C
A 15-car local train with an air turbine ETD is performing a Brake Pipe Leakage Method Test. What is required?
- Close the angle cock between the second-to-last and the last car
- Close the angle cock between the locomotive and train
- Disarm the ETD before conducting the test
- Close the angle cock between the last car and the ETD
Back #61
ABTH 100.9C
Answer: Close the angle cock between the last car and the ETD
Feedback:If you're on a smaller train such as a Local, an air turbine ETD may bleed down your air by more than 5 psi before the test is complete. If that happens, you must close the angle cock between the ETD and last car to get an accurate test.
Front #234
GCOR 9.10
A relief crew boards a train that has been tied down on the main track in CTC. They did not have a briefing with the previous crew and do not know what the previous signal was. Once they depart, how must they proceed?
- Proceed prepared to stop at the next signal until the next signal is visible and that signal displays a Proceed indication
- Proceed at 20 mph until the leading wheels have passed the next governing signal or the end of the block system
- Proceed at restricted speed until the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication and the track to that signal is clear
- Restricted speed until the leading wheels have passed the next governing signal or the end of the block system
Back #234
GCOR 9.10
Answer: Restricted speed until the leading wheels have passed the next governing signal or the end of the block system
Feedback:When the previous signal is unknown, you must proceed at restricted speed because you don't know what is out in front of you or the condition of the track ahead.
Front #226
GCOR 9.8
When may a train comply with the next signal's indication?
- When its aspect can be clearly seen, and the signal governs the track where movement is occurring or will be made
- After passing a Stop and Proceed signal, the next signal is visible, that signal displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
- When the previous signal indication requires movement at restricted speed
- When authorized by the train dispatcher
Back #226
GCOR 9.8
Answer: When its aspect can be clearly seen, and the signal governs the track where movement is occurring or will be made
Feedback:This does not apply when a rule or previous signal indication requires movement at restricted speed. Train crews must comply with the requirements of restricted speed until the leading wheels pass the next governing signal.
Front #235
GCOR 9.12.2
A train is given verbal authority to pass a Stop signal that governs movement over a drawbridge. What must a crew member verify?
- A track permit has been granted
- The bridge is in proper position for the train to pass
- They are following the instructions in the release box
- Track and Time has been granted
Back #235
GCOR 9.12.2
Answer: The bridge is in proper position for the train to pass
Feedback:If the control operator was unable to provide a proceed indication and had to give verbal authority, this could be an indication that the bridge is not in a safe position to pass. That's why a crew member should always check the bridge before proceeding.
Front #343
GCOR 5.8.2
- O (long, short) is the whistle sequence for what indication?
- Public crossing at grade with engine in front
- Starting from stop and people are around
- Approaching men or equipment on or near the tracks
- Persons or livestock are on the track at other than road crossings at grade
Back #343
GCOR 5.8.2
Answer: Approaching men or equipment on or near the tracks
Feedback:- Regardless of any whistle prohibition (quiet zones), the initial warning or heads-up to the men or equipment must be a long followed by a short (- O). - After this initial warning, sound whistle sequence #4 (short, short (O O)) intermittently until the head-end passes. - Do not stop whistling even if the men or equipment try to wave you off.
Front #327
GCOR 5.47
What must the train do when a red flag is displayed between the rails of the track?
- Stop and wait for permission from the dispatcher.
- Continue moving, not exceeding 10 mph.
- Stop and not proceed until flag has been removed.
- Stop and wait for permission from the employee in charge.
Back #327
GCOR 5.47
Answer: Stop and not proceed until flag has been removed.
Feedback:A red flag between the rails protects trains and crew from dangerous conditions. For example, a red flag might be placed between rails for an auxiliary track that is out of service. In this case, the flag protects the train from traversing track that may be defective.
Front #237
GCOR 9.12.3
You are stopped at an automatic interlocking, you have complied with the instructions in the release box, and don't see any conflicting movements. However, the signal still displays a Stop indication. How may you proceed?
- Proceed at maximum authorized speed
- Proceed at prepared to stop
- Proceed at reduced speed
- Proceed at restricted speed
Back #237
GCOR 9.12.3
Answer: Proceed at restricted speed
Feedback:An automatic interlocking is not controlled by a train dispatcher or control operator. The signals work automatically based on train movements approaching the interlocking. If the signal doesn't upgrade to a proceed, that might mean there's a track condition or someone in that block. Moving at restricted speeds ensures the crew can stop short of anything in the block ahead.
Front #161
GCOR 6.4.1
If this train was between block signals, would it need permission to make a reverse movement?
- Permission is not needed if the reverse movement is visually protected
- Yes, permission is always required when making a reverse movement
- Permission is not needed as long as the train remains within the limits of their Track and Time authority
- No, as long as it's within the same signaled block
Back #161
GCOR 6.4.1
Answer: No, as long as it's within the same signaled block
Feedback:- Once a train enters a block, it essentially "owns" that block and can move in either direction within it. - Block signals governing movement into the occupied block will display red aspects thereby protecting the train within the block.
Front #43
ABTH 100.9C
Why is the Air Flow Method the preferred method for conducting a brake pipe leakage test? (Select Best Answer)
- Performing the Brake Pipe Leakage Test in accordance with rule ABTH 100.9 C is obsolete.
- The Air Flow method is a more efficient way to satisfy the required leakage test.
- The Air Flow Method is more accurate than the Brake Pipe Leakage Test (ABTH 100.9 C).
Back #43
ABTH 100.9C
Answer: The Air Flow method is a more efficient way to satisfy the required leakage test.
Feedback:The Air Flow Method is more efficient than using rule ABTH 100.9 C, Brake Pipe Leakage Method. When using the AFM, results of the amount of leakage, if any, in the train is known within a short time of the air being sent through the brake pipe. That time can increase in cold weather. The steps required when using ABTH 100.9 C, at a minimum, require three minutes to complete. The other steps outlined in that rule also require additional time. There is no minimum time to determine leakage when using the AFM. Once the air flow drops below 60 CFM (90 CFM for distributed power trains), the test is complete.
Front #175
GCOR 6.6
Can a back-up move be made into or within yard limits or restricted limits?
- No, unless a JSB is held between the train crew and dispatcher
- Yes
- Yes, as long as the move is protected
- No
Back #175
GCOR 6.6
Answer: No
Feedback:Within yard and restricted limits, trains are authorized to move on the main track not protecting against other trains. The dispatcher is not always aware of train movements within these limits. Protecting against other train movements is a key component in the JSB that occurs between the crew and dispatcher. However, train movements have to be known in order to protect against. In this case, there is no way for the crew or dispatcher to protect the rear of the train making the back-up move into or within yard or restricted limits.
Front #74
ABTH 100.10B
Before or during a Class 1 air brake test, inspect the retaining valves and verify that they are in: Select the best answer.
- Slow direct
- High pressure
- Low pressure
- Exhaust
Back #74
ABTH 100.10B
Answer: Exhaust
Feedback:If the retaining valves are not in the exhaust position, the brakes will remain applied when the automatic brake valve is placed in Release. Exhaust position allows all of the air in the brake cylinder to dissipate thus releasing the brakes. In addition to verifying the position of the retaining valves, inspect angle cocks, air hoses, and the system for any leakage.
Front #86
ABTH 100.13
When is a running air brake test required? Select all that apply.
- On all trains during inclement weather
- On all passenger trains
- On all trains prior to descending mountain grades
- On all trains consisting entirely of business cars
Back #86
ABTH 100.13
Answer: - On all trains consisting entirely of business cars - On all passenger trains - On all trains during inclement weather - On all trains prior to descending mountain grades
Feedback:Testing periodically to make sure no snow or ice builds up on the brake shoes is critical considering the detrimental effects of brakes not functioning properly. Trains on mountain grades can reach dangerous speeds very quickly. Bad weather can have adverse effects on the rail and braking system. Malfunctioning brakes on passenger trains or trains with business cars could put the lives of hundreds of passengers in danger. Testing brakes keeps everyone safe and on the rail.
Front #260
GCOR 14.10
What must be stated when reporting clear of a track warrant?
- Employee's name or other identification, track warrant number being released, limits being released
- Employee's name or other identification, track warrant number being released, miles traveled from the last track warrant
- Employee's name or other identification, time the last track warrant was voided, limits being released
- Train symbol or other identification, time the track warrant was granted, limits being released
Back #260
GCOR 14.10
Answer: Employee's name or other identification, track warrant number being released, limits being released
Feedback:Stating the required information when releasing authority ensures dispatcher does not inadvertently release the wrong authority.
Front #42
ABTH 100.9B
What equipment is required to perform the Air Flow Method (AFM) of testing brake pipe leakage? (Select All That Apply)
- Locomotive with an air flow meter measured in increments no greater than 10 CFM
- Controlling locomotive with a maintaining-type automatic brake valve
- Train with a gauge or device at the rear of the train
- Air flow meter that functions within calibration requirements
Back #42
ABTH 100.9B
Answer: -Controlling locomotive with a maintaining-type automatic brake valve -Locomotive with an air flow meter measured in increments no greater than 10 CFM -Air flow meter that functions within calibration requirements -Train with a gauge or device at the rear of the train
Feedback:All BNSF locomotives have a maintaining-type automatic brake valve. This valve compensates for leakage and keeps the brake pipe pressure from dropping. If the controlling locomotive does not have the required equipment to perform the Air Flow Method to test for leakage, then use ABTH 100.9C Brake Pipe Leakage Method to properly perform the required leakage test.
Front #200
GCOR 6.28
The turnout speed for a non-controlled siding is 30 mph. How must a train move in that siding?
- At a speed that allows stopping within half the range of vision not exceeding 10 mph
- At a speed that allows stopping within half the range of vision, not exceeding 30 mph
- Restricted speed
- Train speed, track speed
Back #200
GCOR 6.28
Answer: At a speed that allows stopping within half the range of vision, not exceeding 30 mph
Feedback:- Because the train is moving on a non-controlled siding, the train is governed by Rule 6.28 - However, the turnout speed dictates the maximum authorized speed in the siding - Therefore, the train may move at 30 mph, but the requirement to stop within half the range of vision short of TERMSD still exists
Front #94
ABTH 101.2A
The locomotive cab card indicates the locomotive was inspected the previous day. When should the current day's inspection be completed?
- Before 2159
- Before 2259
- Before 2359
- Before 1259
Back #94
ABTH 101.2A
Answer: Before 2359
Feedback:If the locomotive had an inspection on the previous day, the engineer needs to complete a daily inspection before 2359 unless relieved by the proper authority.
Front #340
GCOR 5.8.1
Which of the following are instances of when you should ring your engine bell? (Select all that apply.)
- Before moving, except when switching
- When operating in a Work Between area in TWC territory
- As a warning signal anytime it is necessary
- When approaching railroad crossings at grade
Back #340
GCOR 5.8.1
Answer: - Before moving, except when switching - As a warning signal anytime it is necessary
Feedback:- When you're stopped and before you start moving, turn your engine bell on to let anyone in the surrounding area know you're about to start moving - The bell is a good warning signal to alert people of your presence - Never hesitate to turn on your bell
Front #233
GCOR 9.12.1
You are stopped at a controlled signal in CTC and no conflicting movement is evident. What is required?
- Contact the control operator unless the train is within Track and Time limits or entering Track and Time limits from any point other than either end of Track and Time limits
- Assume the control operator knows where the train is and wait for the signal to display a Proceed indication
- Contact the employee in charge to receive instructions beyond the Stop indication
- Proceed at restricted speed until the leading wheels pass the next signal
Back #233
GCOR 9.12.1
Answer: Contact the control operator unless the train is within Track and Time limits or entering Track and Time limits from any point other than either end of Track and Time limits
Feedback:If no conflicting movement is evident, you must contact the control operator. It may mean something is occurring in the block ahead. It is also possible they simply forgot to give you further authority.
Front #185
GCOR 6.5
Which of the following movements do not require permission?
- Backup movement
- Shoving movement
- Reverse movement outside of same signaled block
- All movements require permission
Back #185
GCOR 6.5
Answer: Shoving movement
Feedback:A reverse move made outside of the train's signaled block always requires permission. Backup moves always require permission from control operator or train dispatcher. There are no exceptions to this rule. Shove movements can be made on any track. No permission is required to make a shove move.
Front #258
GCOR 14.2
Track warrant limits must be designated by specifying track, where required, and specific locations. Which of the following can be used as specific locations on a track warrant? Select all that apply.
- Mileposts
- Switches
- Railroad identifiable points
- Trackside warning detectors
Back #258
GCOR 14.2
Answer: -Mileposts -Railroad identifiable points -Switches
Feedback:When designating limits on a track warrant, a switch (e.g., ESS Anna). a milepost (e.g., MP 55), or a railroad identifiable point (e.g., Station Sign Cloy) may be used to indicate the specific locations.
Front #73
ABTH 100.10A
A Class 1 air brake test is required on any portion of the train that has not been kept charged (off air over ____ hours). Select the best answer.
- 24
- 2
- 12
- 4
Back #73
ABTH 100.10A
Answer: 24
Feedback:Any previous Class 1 air brake test is void if a car has been off air for more than 24 hours making it necessary to conduct a Class 1 air brake test on the portion of the train that has not been kept charged.
Front #218
GCOR 9.5
What must the crew do if a train overruns any block signal that requires it to stop? (Select all that apply)
- Warn other trains at once by radio.
- Reduce to restricted speed.
- Stop the train immediately.
- Report it to the train dispatcher.
Back #218
GCOR 9.5
Answer: -Report it to the train dispatcher. -Warn other trains at once by radio. -Stop the train immediately.
Feedback:The first thing to do is make an emergency broadcast over the radio to warn others. Another train could be approaching the location, it requires sufficient warning to come to a stop.
Front #126
ABTH 102.13.1
Distributed Power trains are considered to have an en route failure when the loss of communication has exceeded ___ minutes as indicated by the control console for a lead controlling distributed power locomotive at the head end of a train.
- 1
- 5
- 10
- 2
Back #126
ABTH 102.13.1
Answer: 5
Feedback:When the Comm message appears on distributed power trains, it is important to note when it came on. If on for 5 minutes, it is considered an en route communication failure, and compliance with applicable rules is required.
Front #321
GCOR 5.4.3B
Two miles beyond the yellow-red flag, no red flag is present. What is required of the crew?
- Stop and wait for permission from the dispatcher.
- Move at restricted speed.
- Continue moving, not exceeding 10 mph.
- Stop and wait for instruction from the employee in charge of the yellow-red flag.
Back #321
GCOR 5.4.3B
Answer: Move at restricted speed.
Feedback:- Crew members must be prepared to stop short of a red flag two miles beyond the yellow-red flag. - Moving at a speed that allows stopping within half the range of vision will protect employees who might be working on the track ahead. - Until it is confirmed that no restriction is in effect, proceed through that area as if restrictions are in place.
Front #147
ABTH 103.5
To prevent locomotive brakes from applying when initiating an automatic brake application or when making additional split reductions, actuate the independent brake valve a minimum of ___ seconds prior to a brake pipe reduction and continue until exhaust stops, but no less than ___ continuous seconds for each brake pipe reduction.
- one; 10
- one; five
- two; 10
- two; five
Back #147
ABTH 103.5
Answer: two; 10
Feedback:It is important to actuate before making an automatic brake pipe reduction and after the exhaust stops, but not less than 10 seconds for each brake pipe reductions to prevent air from reaching the brake cylinders.
Front #171
GCOR 6.4
Can a train make a reverse movement on a controlled siding while remaining in the same signaled block?
- Yes, per GCOR 6.4
- No, a reverse movement can only be made on the main track
- Yes, with permission from the control operator
- Yes, with authority from the control operator
Back #171
GCOR 6.4
Answer: Yes, per GCOR 6.4
Feedback:Controlled sidings require either verbal authority or a controlled signal displaying a Proceed indication to enter. Unless Track and Time was granted in the controlled siding, the authority is in one direction, which means it is possible to move opposite the authorized direction. Since the train crew is making this move within the same signaled block, no permission from the control operator is required. If the train crew were to go outside of their same signaled block, permission from the control operator would be necessary.
Front #267
GCOR 14.7
A train in non-signaled TWC must know the train is complete before releasing or reporting past a specific location. Which of the following is an acceptable way to determine the train is complete. (Select all that apply.)
- An inspection while stopped verifies marker is on the rear car of the train
- Trackside warning detector transmits an axle count for the train and the axle count duplicates the axle count previously transmitted by the previous trackside warning detector
- A crew member can observe the rear car on which the marker is placed, or an employee verifies the marker is on rear
- The rear of the train has a rear-end telemetry device, and air pressure on the head-end device indicates brake pipe continuity
Back #267
GCOR 14.7
Answer: - The rear of the train has a rear-end telemetry device, and air pressure on the head-end device indicates brake pipe continuity - An inspection while stopped verifies marker is on the rear car of the train - A crew member can observe the rear car on which the marker is placed, or an employee verifies the marker is on rear - Trackside warning detector transmits an axle count for the train and the axle count duplicates the axle count previously transmitted by the previous trackside warning detector
Feedback:In non-signaled territory, knowing the train is complete is especially important. If authority is released and any part of the train is still on the track behind you, there is no signal warning the train behind you that there may be an obstruction on the track.
Front #81
ABTH 100.10.1
How many miles can trains designated as extended haul travel without stopping for an air brake test?
- Not more than 2,000 miles
- Not more than 1,500 miles
- Not more than 3,000 miles
- Not more than 2,500 miles
Back #81
ABTH 100.10.1
Answer: Not more than 1,500 miles
Feedback:An extended haul designation reduces required stops and inspections at intermediate points. However, before the train exceeds 1,500 miles, another Class 1 or Class 1A air brake test must be performed by a Qualified Mechanical Inspector (QMI).
Front #1
ABTH 103.4
When transitioning from dynamic brake mode to power mode, wait ____ seconds in _____ before advancing throttle to a power position.
- 5; Idle
- 10; Setup
- 10; Idle
- 8; Idle
Back #1
ABTH 103.4
Answer: 10; Idle
Feedback:This will allow the train to absorb in-train forces and to turn over from dynamic brake mode to power mode.
Front #219
GCOR 9.7
When a block is occupied, or when a switch protected by a signal is changed from its normal position and that signal fails to display its most restrictive indication, what are you required to do?
- Proceed at restricted speed, notify the Trainmaster immediately, and warn others by radio of the exact location and status of the train
- Regard the signal as displaying Stop, stop the train immediately, and warn others by radio of the exact location and status of the train
- Proceed at reduced speed, notify the dispatcher immediately, and warn others by radio of the exact location and status of the train
- Proceed at restricted speed, notify the dispatcher immediately, and warn others by radio of the exact location and status of the train
Back #219
GCOR 9.7
Answer: Regard the signal as displaying Stop, stop the train immediately, and warn others by radio of the exact location and status of the train
Feedback:- This is otherwise known as a "false clear" - The train must stop immediately, and employees must warn others by radio of the exact location and status of train - Do not move the train without permission.
Front #238
GCOR 9.12.4A
A train authorized beyond a Stop signal in ABS may proceed at restricted speed under which of the following conditions? (Select all that apply.)
- Train is granted Track and Time.
- Authority beyond the signal is joint with other trains or employees.
- Granted permission from dispatcher to pass the signal. If dispatcher can't be contacted, move 100 feet past signal, wait 5 minutes, then proceed at restricted speed
- To couple to its train or to a standing cut of cars if track between engine and cars is clear.
Back #238
GCOR 9.12.4A
Answer: - Authority beyond the signal is joint with other trains or employees. - To couple to its train or to a standing cut of cars if track between engine and cars is clear. - Granted permission from dispatcher to pass the signal. If dispatcher can't be contacted, move 100 feet past signal, wait 5 minutes, then proceed at restricted speed.
Feedback:Except in 9.14 territory, signals in ABS govern movements; they do not authorize movement. Note that in this scenario, the train must already have authority on the track to exercise any of these options.
Front #88
ABTH 100.13
What should you do when conducting a running air brake test and the brakes are not working properly? Select the best answer.
- Release the air and attempt another running air brake test
- Attempt an application and release air brake test (Class 3)
- Stop the train immediately, using all available braking
- Stop the train and conduct a Class 1 air brake test
Back #88
ABTH 100.13
Answer: Stop the train immediately, using all available braking
Feedback:If a train is not slowing down as it should, immediately stop using all available braking including dynamic braking, a full-service brake application, and, if necessary, an emergency brake application.
Front #319
GCOR 5.4.3B
When a yellow-red flag is displayed and no restriction is in effect as specified by a track bulletin, crew members must be prepared to stop short of a red flag:
- Three miles beyond the yellow-red flag
- Four miles beyond the yellow-red flag
- Two miles beyond the yellow-red flag
- One mile beyond the yellow-red flag
Back #319
GCOR 5.4.3B
Answer: Two miles beyond the yellow-red flag
Feedback:Even when it's not in writing, crew members must respond to an unannounced yellow-red flag prepared to stop for a red flag. With the potential for people to be working on the track ahead, the crew must operate in a manner that ensures everyone's safety.
Front #263
GCOR 14.1
From whom do you request a track warrant?
- Dispatcher
- Employee in charge
- Yardmaster
- Trainmaster
Back #263
GCOR 14.1
Answer: Dispatcher
Feedback:Per GCOR 14.1, where designated by the timetable, a track warrant will authorize main track use under the direction of the train dispatcher.
Front #197
GCOR 6.27
When required to move at restricted speed, a train is not required to stop short of which of the following?
- Men or equipment fouling the track
- Derail or switch lined improperly
- Train
- Broken rail
Back #197
GCOR 6.27
Answer: Broken rail
Feedback:Broken rail can require a train to move at restricted speed. Most broken rail is very difficult to see, especially from the cab of an engine. While a train is not required to stop in half the range of vision for broken rail, the crew must maintain a lookout for it and, if possible, stop prior to it.
Front #168
GCOR 6.4.2B
Can the BNSF train change direction with the limits of the automatic interlocking? (Select All That Apply)

- Yes, as long as one set of trucks from a railcar occupies the interlocking limits
- Yes, with permission from the control operator
- Yes, as long as one car length occupies the interlocking limits
- No, a reverse move can't be made within an automatic interlocking
Back #168
GCOR 6.4.2B
Answer: Yes, as long as one car length occupies the interlocking limits
Feedback:Unlike manual interlockings, Automatic Interlockings are not controlled, and the signals operate based on train movements. As long as one car occupies the limits of the interlocking, the opposing signals governing movement into the interlocking cannot display Proceed indications.
Front #192
GCOR 6.23
What must a crew member do when a train or engine is stopped by an emergency application of the brakes, and an adjacent main track or controlled siding may be obstructed? (Select all that apply.)
- Immediately warn other trains by radio, stating the exact location and status of the train and repeat as necessary.
- Place lighted fusees on the track the train is on.
- Place lighted fusees on the adjacent tracks.
- Notify the train dispatcher or control operator and, when possible, foreign line railroads, if necessary.
Back #192
GCOR 6.23
Answer: - Immediately warn other trains by radio, stating the exact location and status of the train and repeat as necessary. - Notify the train dispatcher or control operator and, when possible, foreign line railroads, if necessary. - Place lighted fusees on the adjacent tracks.
Feedback:An emergency brake application occurs because of a dangerous or potentially dangerous condition. Any time the train experiences an emergency application, whether crew-induced or undesired, the train crew must provide warning on adjacent main tracks or controlled sidings. Warning messages should be in accordance with rule 2.10 by stating "Emergency" three times over the radio. This also applies if the train has actuated a shifted load or is dragging an equipment detector.
Front #138
ABTH 103.3A
When applying or reapplying the automatic brakes to control speed, the brake pipe reduction should be __ psi or less.
- 26
- 15
- 10
- 20
Back #138
ABTH 103.3A
Answer: 15
Feedback:15 psi is almost 60% of total service braking. Needing any more force could indicate a dangerous malfunction in the braking system such as a blocked brake. If more than a 15 psi reduction is necessary to control speed, the crew must stop and determine why.
Front #338
GCOR 5.4.8
Track flags do not apply to the track on which the train is moving when:
- They are displayed in the middle of the track the train is on.
- They are displayed to the right.
- They are displayed to the left.
- They are displayed beyond the first rail of the adjacent track.
Back #338
GCOR 5.4.8
Answer: They are displayed beyond the first rail of the adjacent track.
Feedback:- When flags are displayed beyond the first rail of an adjacent track, the flags do not apply to the track on which the train is moving. - For example: If you were sitting on a train on main track one and another train is stopped next to you on main track two, you would be unable to see a flag on the other side of main track 2. Anything beyond the first rail of a track next to you does not apply to your track.
Front #79
ABTH 100.10.2
If a train has been off air less than 24 hours and the yard test plant pressure setting is less than the locomotive regulating valve, what is required? (Select all that apply.)
- An Initial Terminal and Road Air Brake Test
- A Brake Pipe Leakage Test
- An Application and Release Air Brake Test
- An Intermediate Air Brake Test
Back #79
ABTH 100.10.2
Answer: - A Brake Pipe Leakage Test - An Application and Release Air Brake Test
Feedback:If a train is off air 24 hours or less and the yard test plant pressure setting is less than the locomotive regulating valve, you must: - Charge the air to the regulating valve setting - Perform a Brake Pipe Leakage Test - Perform an Application and Release Air Brake Test (Class 3 Air Brake Test)
Front #251
GCOR 14.2B
A track warrant states, "Proceed from MP 555 to Piper on the main track." No siding exists at Piper. Where does the authority extend to at Piper?
- East Siding Switch Piper
- The MP sign closest to Piper
- West Siding Switch Piper
- Station Sign Piper
Back #251
GCOR 14.2B
Answer: Station Sign Piper
Feedback:-Authority extends to, but not beyond, the Station Sign at Piper -No siding exists at Piper, therefore, no siding switches -Station Sign at Piper is an identifiable point
Front #194
GCOR 6.23
BNSF Train A made an emergency radio call near MP 25.6. BNSF Train B is approaching MP 25.6 and has heard the radio call. How must BNSF Train B approach this location?
- Restricted speed
- 20 mph
- Governed by signal indication
- 10 mph
Back #194
GCOR 6.23
Answer: Restricted speed
Feedback:A train on an adjacent track that receives radio notification must pass the location specified at restricted speed prepared to stop short of fouling equipment. Restricted speed ensures the train is able to safely pass the other train and crew members. The train may resume maximum authorized speed once the leading wheels reach the opposite end of the train in emergency.
Front #345
GCOR 5.8.3
How should the crew proceed with movement of the train if a whistle fails?
- Ring the bell once and continue on.
- Proceed slowly through each public crossing.
- Stop the train before each public crossing.
- Ring bell continuously.
Back #345
GCOR 5.8.3
Answer: -Ring bell continuously. -Stop the train before each public crossing.
Feedback:Sometimes mechanical failures happen en route, so extra steps are necessary to alert the public a train is entering a crossing. If there are no motorists in the vicinity or the gates are down to protect, it is not necessary to have an employee on the ground.
Front #145
ABTH 103.3B
An eastbound train is stopped in a siding to meet a westbound train. When operating conditions allow, when is it permitted for the eastbound train to release the brakes?
- Once at least half of the westbound train has passed
- Once stopped, the engineer may release brakes at any time
- As soon as the westbound train passes, regardless of signal indication
- When the train is ready to depart
Back #145
ABTH 103.3B
Answer: When the train is ready to depart
Feedback:If required to release brakes, such as during a train inspection, brakes must be reapplied and released prior to departing. An example of an operating condition that may not allow brakes to remain applied until ready to depart or no increase in brake pipe reduction after stopping: when near a long, descending heavy or mountain grade and brake system requires full charge before proceeding.
Front #337
GCOR 5.4.8
When track flags are used, where are they displayed in multiple main track territory or where sidings are adjacent to the main track?
- They are displayed to the right of the track as viewed from an approaching train.
- They are placed beyond the first rail of the adjacent track.
- They are placed beyond the furthest rail of the adjacent track.
- They are placed on the field side of the outside tracks.
Back #337
GCOR 5.4.8
Answer: They are placed on the field side of the outside tracks.
Feedback:- Flags are placed in this manner unless otherwise specified by track bulletin, track warrant, special instructions, or general order. - Examples of track flagging are provided in Appendix A of the System Special Instructions.
Front #112
ABTH 102.1.3
A train separation has occurred causing an emergency brake application. What step must be performed first when a separation occurs?
- Immediately determine the availability of the rapid responder.
- Determine what tools will be needed to make repairs and recharge the air brake system.
- Close the angle cock on the rear car of the portion attached to the lead locomotive consist.
- Immediately secure detached portions.
Back #112
ABTH 102.1.3
Answer: Immediately secure detached portions.
Feedback:When a train separation occurs, the detached portion must be secured with hand brakes before repairs are made or the air brake system is recharged. Never depend on the air brake system for securement because the air can bleed off the cars. This would cause the brakes to release. Any increase in brake pipe pressure can also trigger a release.
Front #183
GCOR 6.5
A train crew is shoving cars on the main track in the authorized direction. The last signal they passed was displaying a Proceed indication. The maximum timetable speed is 45 mph. What is the maximum speed at which the cars can be shoved?
- 45 mph
- 40 mph
- 20 mph
- Restricted speed
Back #183
GCOR 6.5
Answer: 20 mph
Feedback:Since the train crew is on the main track and shoving in the authorized direction, the crew is allowed to shove at a speed not exceeding 20 mph. Although shoving at 20 mph is allowed, the crew members need to move at a speed that allows them to protect the shove to avoid any incidents.
Front #193
GCOR 6.23
A 12,000-ton loaded grain train, has experienced an undesired emergency application of the brakes. The train was moving at 15 mph when the emergency application occurred, and the crew experienced no severe slack action. Brake pipe pressure has been restored to the rear of the train. What is required from the crew before proceeding?
- The crew can make a roll-by inspection of their entire train before proceeding.
- The crew is not required to inspect their train before proceeding.
- The crew must make a walking inspection of their entire train before proceeding.
- The crew is only required to inspect half of their train, by the safest means, before proceeding.
Back #193
GCOR 6.23
Answer: The crew is not required to inspect their train before proceeding.
Feedback:A solid loaded bulk commodity train that experiences no severe slack action while stopping and brake pipe pressure restores is one of the exemptions relieving visual inspection of the train. To be exempt from visual inspection, a train must meet one of the four exemptions. It also must experience no slack action and brake pipe pressure must be restored to the rear
Front #146
ABTH 103.3B
A train stopped on the main track is ready to depart. The engineer releases the automatic brakes and realizes the ETD is not showing brake pipe pressure being restored to the end of the train. If the train needs to be moved to check for ETD failure, movement must not:
- Exceed 5 mph and the distance specified by the train dispatcher
- Exceed 5 mph and the train's length
- Exceed 10 mph and the train's length
- Exceed 10 mph and the distance specified by the train dispatcher
Back #146
ABTH 103.3B
Answer: Exceed 10 mph and the train's length
Feedback:Movement may exceed the length of train to prevent blocking public crossings or stopping on a bridge not equipped with walkways.
Front #6
ABTH 100.8
When conducting an inspection to determine if the brakes apply and release on the rear car, the brakes should apply with a brake pipe pressure decrease of _____ and release with brake pressure increase of _____.
- 5 psi and 3 psi
- 10 psi and 10 psi
- 10 psi and 3 psi
- 5 psi and 5 psi
Back #6
ABTH 100.8
Answer: 5 psi and 5 psi
Feedback:It is not always practical to have an employee at the rear of the train to verify the brakes apply and release on the last car, so other methods are in place to assist. The drop of 5 psi on the rear indicates the brakes are set and the increase in 5 psi verifies the release.
Front #167
GCOR 6.4.2A
The head end of a BNSF locomotive has stopped between the outer opposing signals of a control point. Does the BNSF train need permission to change?
- No, the locomotive needs permission to make a reverse movement
- Yes, because now the locomotive is now considered the trailing end of the movement.
- The locomotive needs authority to change direction within the control points
- No
Back #167
GCOR 6.4.2A
Answer: No
Feedback:The locomotive is still the leading end of the movement. The trailing end is still the rear car. Since the rear car did not stop within the control points, the train needs no permission to change direction. This would be considered making a reverse move within the same signaled block.
Front #184
GCOR 6.5
Before a shoving movement can begin, what two pieces of information must be relayed to the engineer?
- Type of cars being shoved
- How the shove is being protected
- Who is protecting the shove
- Position of derails or switches improperly lined
Back #184
GCOR 6.5
Answer: - Who is protecting the shove - How the shove is being protected
Feedback:It's imperative the engineer know which crew member is going to protect the shove movement. That crew member is essentially the eyes of the engineer and is jointly responsible for the safety of the shove move.
Front #11
ABTH 103.6.3B
A crew is approaching a permanent speed restriction on a level grade with the slack bunched. The engineer will be using only air brakes to slow down. With the throttle in Idle, the engineer will make a __________ at a sufficient distance from the speed restriction.
- Full service brake pipe reduction
- Minimum brake pipe reduction
- 20-psi brake pipe reduction
- 15-psi brake pipe reduction
Back #11
ABTH 103.6.3B
Answer: Minimum brake pipe reduction
Feedback:When air brakes are used to control train speed, begin with a minimum reduction, and then use split reductions of 2?3 psi spaced 30 seconds apart for additional brake pipe reductions.
Front #249
GCOR 9.17
A train wants to enter the main track within CTC where no governing signal exists. What must happen before opening the main line switch?
- Open the switch, move 100 feet onto the main track, wait 5 minutes, then proceed at restricted speed
- Open the switch, wait 5 minutes, then proceed not exceeding 20 mph
- Open the switch, wait 5 minutes, then proceed at maximum authorized speed
- The control operator must verify that there are no conflicting movements before giving the authority
Back #249
GCOR 9.17
Answer: The control operator must verify that there are no conflicting movements before giving the authority
Feedback:To enter CTC, a train can only be authorized to do so by a controlled signal displaying a Proceed indication or by receiving verbal authority is in one of the following ways: - Movement past a Stop signal per 9.12.1 - Verbal authority to enter the main track between block signals - Granted Track and Time under rule 10.3
Front #264
GCOR 14.1
When in effect, where must track warrant instructions be followed? (Select all that apply.)
- Other than main track
- CTC
- Yard limits
- Restricted limits
Back #264
GCOR 14.1
Answer: - Yard limits - Restricted limits
Feedback:Per GCOR 14.1, track warrant instructions must be followed where yard limits or restricted limits are in effect. The track warrant may provide specifics like a Box 11 to not exceed 10 mph between two locations or a Box 10 to clear the main track by a certain time. The train must still operate based in 6.13 YL or 6.14 RL rules.
Front #344
GCOR 5.8.2
What is the whistle sequence for approaching a public crossing at grade with the engine in front?
- O O O O O O (short, short, short, short, short, short )
- - - O - (long, long, short, long)
- - O (long, short) followed by O O (short, short) intermittently
- - - O O - - (long, long, short, short, long, long )
Back #344
GCOR 5.8.2
Answer: - - O - (long, long, short, long)
Feedback:This whistle must be prolonged or repeated as necessary until the engine completely occupies the crossing(s). Not all public crossings have gates or lights. Sounding the whistle is an additional procedure to help ensure the safety of the crews and the public.
Front #127
ABTH 102.13.1
A crew is operating a conventional train on a track that is NOT identified in System Special Instructions Item 2A. Communication with the ETD is lost. What is required?
- Train must not exceed 30 mph until the failure is corrected or another method of compliance is secured
- Train may continue moving at maximum track speed until it reaches the next terminal
- Train must stop and not proceed until the failure is corrected or another method of compliance is secured
Back #127
ABTH 102.13.1
Answer: Train must not exceed 30 mph until the failure is corrected or another method of compliance is secured
Feedback:Tracks listed in System Special Instructions Item 2(A) require the train to stop and not proceed until the issue is corrected. The tracks listed in SSI Item 2(A) are tracks that have a grade of 2% or greater. That is why trains need to stop and not proceed until failure is corrected or another method of compliance is secured.
Front #137
ABTH 103.3A
When applying automatic brakes using split reductions for a planned slowdown or stop, make an initial reduction of six to eight psi followed by additional reductions in ______ psi increments, spaced ____ seconds apart.
- 2-3; 20
- 4-6; 3
- 2-3; 30
- 4-6; 20
Back #137
ABTH 103.3A
Answer: 2-3; 30
Feedback:For planned slowdowns and stops, after the initial reduction of six to eight psi, make additional reductions in two to three psi increments. These reductions should be spaced 30 seconds apart to give the system time to stabilize, which results in better train handling. Make a final brake pipe reduction when operating conditions permit as train is nearing a stop to prevent a run-out of slack. This results in brake pipe pressure exhausting as the train comes to a stop.
Front #342
GCOR 5.8.2
O O O O O O O (succession of short sounds) is the whistle sequence for which indication?
- Starting from stop and people are around
- People or livestock are on the track at other than road crossings at grade
- Approaching men or equipment on or near the track
- Public crossing at grade with engine in front
Back #342
GCOR 5.8.2
Answer: People or livestock are on the track at other than road crossings at grade
Feedback:When there are people or livestock on the tracks and you're not at a road crossing, make several short whistle bursts to get their attention.
Front #318
GCOR 5.4.3A
When yellow-red flags are used and they are displayed less than two miles from the restricted area, how will this be communicated to the crew on the BNSF?
- This information will be included in the track bulletin.
- This information will be included in a general notice.
- This information will be included in a general order.
- This information will be included in the track warrant.
Back #318
GCOR 5.4.3A
Answer: This information will be included in the track bulletin.
Feedback:- When the restricted area is close to a terminal, junction, or another area, employees will display the yellow-red flag less than two miles before the restricted area. - This information will also be included in the track bulletin, track warrant, or general order. - On the BNSF, this information will be in the track bulletin contained within the General Track Bulletin.
Front #232
GCOR 9.12.1
BNSF 8802 is stopped for a red signal at EBCS Hendon Grove and receives these instructions: "After stopping, BNSF 8802 East at east Hendon Grove has authority to pass signal displaying a Stop indication for eastward movement." How must you proceed?
- Proceed at restricted speed until leading wheels pass the next governing signal.
- Proceed at maximum authorized speed.
- Proceed prepared to stop at the next signal until it is visible and displays a Proceed indication.
- Proceed at 20 mph until leading wheels pass the next governing signal.
Back #232
GCOR 9.12.1
Answer: Proceed at restricted speed until leading wheels pass the next governing signal.
Feedback:- After being authorized to pass the Stop indication, you must proceed at restricted speed. - Restricted speed is required because something is causing the signal to be red. A few examples: Train, improperly lined switch, broken rail.
Front #23
ABTH 103.6.3F
When necessary to use stretch braking, exceeding throttle position ___ is prohibited.
- 4
- 3
- 1
- 2
Back #23
ABTH 103.6.3F
Answer: 4
Feedback:Exceeding throttle position 4 is referred to as power braking and is not permitted. Power braking quickly elevates wheel temperatures which could result in damage to equipment and rail.
Front #259
GCOR 14.2
A track warrant states, "Proceed from MP 55 to Anna on the main track. " No siding exists at Anna. Where does the authority extend to at Anna?
- The MP sign closest to Anna
- The station sign at Anna
- East siding switch Anna
- West siding switch Anna
Back #259
GCOR 14.2
Answer: The station sign at Anna
Feedback:No siding exists at Anna, therefore there are no siding switches to use as identifiable points. Authority extends to, but not beyond, the station sign where no siding exists.
Front #353
GCOR 5.9.4
When locomotives are moving, what train light must crew members turn on?
- Cab light
- Headlight to the front
- Ditch lights
- Light on the end coupled to cars
Back #353
GCOR 5.9.4
Answer: Headlight to the front
Feedback:The front headlight display helps improve visibility to the crew operating the train. It can also act as a warning to other crews and the public that a train is approaching. If possible, the crew should also turn on the light at the rear though they may dim or extinguish it on the end coupled to cars.
Front #281
GCOR 14.3
A train operating with a track warrant to proceed from MP 1 to MP 100 is instructed to report passing MP 50. Once reporting past MP 50, how is the authority considered up to that point?
- A track warrant may not be voided in increments.
- Track warrant authority between MP 1 and MP 50 is still in effect. Providing that information to the dispatcher is informational only.
- Track warranty authority between MP 51 and MP 100 is now void.
- It is considered void from MP 1 to MP 50.
Back #281
GCOR 14.3
Answer: It is considered void from MP 1 to MP 50.
Feedback:- When a crew reports past a specific location, track warrant authority is considered void up to that point. - A proper job safety briefing between crew members is crucial in determining which location the rear of the train has cleared. - Conductor and engineer must communicate with dispatcher when reporting clear of a track warrant or past a certain location.
Front #148
ABTH 103.5
The independent brake must not be applied while power or dynamic brakes are being used, except: (Select all that apply.)
- To control wheel slips at speeds below 10 mph
- To control wheel slips at speeds above 10 mph
- When starting or stopping, and speed is below the effective range of the dynamic brakes
- When starting or stopping, and speed is above the effective range of the dynamic brakes
Back #148
ABTH 103.5
Answer: - When starting or stopping, and speed is below the effective range of the dynamic brakes - To control wheel slips at speeds below 10 mph
Feedback:Use dynamic brakes to their fullest extent before supplementing with the independent brakes. Extended range dynamic brakes typically lose their effectiveness at speeds of five mph and lower. For wheel slips, don't use the independent brakes at speeds of 10 mph or above. If the brake cylinder box on the screen flashes yellow, it indicates that brake cylinder pressure is building up while traveling at 10 mph or faster.
Front #78
ABTH 100.10.2
A train has received an Initial Terminal Air Brake Test with a yard test plant with a pressure setting of 90 psi. The air from the test plant was disconnected 6 hours before the crew coupled the locomotive consist to the train and cut in the air. Which air test is required after attaching the locomotives and cutting the air in?
- Class 3 Air Brake Test
- Class 1 Air Brake Test
- Class 1A Air Brake Test
- Cutting Off and Recoupling Air Test
Back #78
ABTH 100.10.2
Answer: Class 3 Air Brake Test
Feedback:An Application and Release Air Brake Test can be performed if the train has been off air for 24 hours or less, and the air from the test plant is the same as the locomotive regulating valve setting (90 psi). Note: On the BNSF, all yard test plants use a pressure of 90 psi for air brake tests.
Front #231
GCOR 9.11
A train is approaching a number-plated signal displaying a red aspect. What does that signal require?
- Train must proceed at restricted speed until the next signal is visible, displays a Proceed indication, and the track to that signal is clear
- Train must proceed prepared to stop at the next signal until it is visible and displays a Proceed indication
- Train must proceed at restricted speed until the next signal is visible, and it displays a Proceed indication
- Train must proceed at restricted speed until leading wheels pass the next governing signal
Back #231
GCOR 9.11
Answer: Train must proceed at restricted speed until leading wheels pass the next governing signal
Feedback:Do not take for granted why the signal is red and restricted speed is required. Maintain restricted speed until the leading wheels pass the next governing signal.
Front #164
GCOR 6.4.2
If the trailing end of a train is stopped between the outer opposing absolute signals of the control point, can it change directions without permission?
- No, permission from the control operator is required.
- Yes, permission from control operator is only required when the leading end stops between the outer opposing signals of the control point.
- Yes, as long as the train is within the same signaled block.
Back #164
GCOR 6.4.2
Answer: No, permission from the control operator is required.
Feedback:It depends on which way the train is moving. While the signals cannot change aspects while within the control points, the switch can be lined for a different route. Since the trailing end of this train is stopped between the outer opposing absolute signals of a control point or manual interlocking, the movement must not change direction without permission from the control operator.
Front #306
GCOR 5.4.1
When track flags are not displayed, where is this information found?
- General notice
- General order
- General track bulletin
- Track warrant
Back #306
GCOR 5.4.1
Answer: General track bulletin
Feedback:- When flags are not displayed, this information is included in the track bulletin, track warrant, or general order. - On our railroad, this information is found in the specific track bulletin contained within the general track bulletin. - On other railroads, it may be found in a track warrant containing track bulletins.
Front #85
ABTH 100.10.1
Which air brake test is required at the intermediate point for extended haul trains? Select all that apply.
- Application and release air brake test (Class 3)
- Running air brake test
- Intermediate air brake test (Class 1A)
- Initial terminal and road air brake test (Class 1)
Back #85
ABTH 100.10.1
Answer: - Intermediate air brake test (Class 1A) - Initial terminal and road air brake test (Class 1)
Feedback:When an extended haul train is at an intermediate point, it requires either a Class 1 or Class 1A Air Brake Test. 100% of the brakes must be operative before departing. The Class 1 or Class 1A Air Brake Test must be performed by a Qualified Mechanical Inspector on trains designated as Extended Haul.
Front #75
ABTH 100.10B
Any cars whose brakes release prematurely may be retested _______ to determine whether the brakes will remain engaged for a minimum of _______ minutes. Select the best answer.
- Three; three
- Twice; two
- Once; two
- Once; three
Back #75
ABTH 100.10B
Answer: Once; three
Feedback:Cars may only be retested once. If the brakes do not remain engaged for a minimum of three minutes during the retest, the car needs to be set out.
Front #341
GCOR 5.8.1
As you approach a quiet zone, what must you do at the crossing sign?
- Start whistle signal (7)
- Apply the train brakes
- Turn on the engine bell
- Reduce throttle
Back #341
GCOR 5.8.1
Answer: Turn on the engine bell
Feedback:Always turn your engine bell on at the whistle board. When operating through a quiet zone, you won't sound the whistle, but the bell is required to be on.
Front #76
ABTH 100.10C
When cars are picked up, inspected, and air tested enroute, which record is required? Select the best answer.
- An electronic record of the class 1 air brake test is required
- No written or electronic record is required
- A written record of the class 1 air brake test is required
Back #76
ABTH 100.10C
Answer: No written or electronic record is required
Feedback:A written or electronic record is required when the air brake test is done by someone other than the crew. In this example, the train crew performed the air brake test, so no written or electronic record is required. However, reporting the test via the Mobile Train Reporting (MTR) app or Voice Train Reporting (VTR) system is required.
Front #176
GCOR 6.6
A train stops on the main track to inspect a car for a potential defect. Once the conductor completes the inspection, which is the most efficient movement that would get the conductor back on the head end?
- Reverse
- Shove
- Back-up
Back #176
GCOR 6.6
Answer: Back-up
Feedback:Reverse and shove movements require visual protection in order to be performed. If the conductor has to provide visual protection for these moves, how can the conductor ever get back on the head end? A back-up move requires no visual protection from the train crew and would be the most efficient movement to make to get the conductor on the head end.
Front #348
GCOR 5.9.2
At the front of every train, the headlight must be set to bright. When must they be turned off? (Select all that apply.)
- Stopped clear of the main track
- Stopped in block system limits, at the radio request of the crew of an approaching train
- Left unattended on the main track in block system limits
- Left unattended on the main track in non-signaled territory
Back #348
GCOR 5.9.2
Answer: - Stopped clear of the main track - Left unattended on the main track in block system limits - Stopped in block system limits, at the radio request of the crew of an approaching train
Feedback:- Even though the rule book lists two times you can turn off your headlight, there are actually three times that it's allowed - The third time it's allowed, as noted in GCOR 5.9.1 (3), is at the radio request of the crew of an approaching train - Don't take the liberty of turning it off unless you are specifically requested to do so by the approaching train
Front #265
GCOR 14.1
A crew needs to enter the main track in TWC-ABS territory. Which one of the following will grant the crew authority onto the main track?
- Track and Time form
- Signal that displays a Proceed indication
- Track permit form
- Track warrant form
Back #265
GCOR 14.1
Answer: Track warrant form
Feedback:- A track warrant form is required to authorize a train to enter or occupy TWC in signaled and non-signaled territory. - Signals govern movement in TWC-ABS; they do not authorize the movement
Front #320
GCOR 5.4.3B
Two miles beyond the yellow-red flag, a red flag is displayed. What is required of the crew?
- Proceed, not exceeding 10 mph.
- Stop short of the red flag.
- Proceed at restricted speed.
- Stop short of the red flag and then proceed at restricted speed.
Back #320
GCOR 5.4.3B
Answer: Stop short of the red flag.
Feedback:- When approaching a red flag, the train must stop short of the red flag and not proceed unless the employee in charge gives instructions, including the milepost location of the red flag. - A train dispatcher cannot grant permission for a train to pass a red flag. - A train dispatcher can relay information regarding passing a red flag from the employee in charge of the red flag.
Front #310
GCOR 5.4.2A
When yellow flags are used, how far in advance of the restricted area should they be displayed?
- Four miles
- One mile
- Two miles
- Three miles
Back #310
GCOR 5.4.2A
Answer: Two miles
Feedback:When yellow flags are used, employees must display a yellow flag two miles before the restricted area to ensure train movement is restricted at the right location.
Front #199
GCOR 6.28
Which of the following is an example of where 6.28 is applicable?
- Main track in CTC territory
- Yard track
- Controlled siding
- Main track in TWC territory
Back #199
GCOR 6.28
Answer: Yard track
Feedback:- If it is not a main track or a controlled siding, the track is considered other than main track. - Examples include yard tracks, industry tracks, and tracks within mechanical facilities. - A non-controlled siding is also considered other than main track.
Front #80
ABTH 100.10.2
If a train has been off air more than 24 hours, what is required?
- An Initial Terminal and Road Air Brake Test (Class 1)
- A Running Air Brake Test
- An Intermediate Air Brake Test
- An Application and Release Air Brake Test
Back #80
ABTH 100.10.2
Answer: An Initial Terminal and Road Air Brake Test (Class 1)
Feedback:A brake system that has not been connected to a continuous source of compressed air of at least 60 psi for 24 hours or more is considered "off air." This requires charging the brake system and performing a Class 1 to verify that all the brakes function correctly on each car.
Front #236
GCOR 9.12.2
Which of the following are methods used to grant authority at a manual interlocking? (Select all that apply.)
- Hand signal from the control operator
- Control signal displaying a Proceed indication
- Crew is granted a track warrant
- Control operator grants verbal authority by the signal
Back #236
GCOR 9.12.2
Answer: - Control signal displaying a Proceed indication - Hand signal from the control operator - Control operator grants verbal authority by the signal
Feedback:Before entering or continuing into CTC territory, the manual interlocking (drawbridge) operator must be sure that the CTC control operator has given authority to proceed.




